Rabbit Housing
Introduction
Make plans for housing before you purchase your rabbits. Housing can be a cage in the garage, a hutch in the backyard or a special building with cages for a number of animals.
The first step is to decide how many rabbits you want to raise and for what purpose. Check with local rabbit breeders to find out about the different breeds and market for rabbits.
Best Management Practices
Once you decide what use that you are going to raise your rabbits for then it is time to start mapping out the housing requirements. The best homemade rabbit cages are built of welded wire. Wire cages are more durable than wooden cages and are less expensive in the long run. Wire cages reduce the incidence of disease because they are easier to clean and disinfect. Wood is not recommended for cage construction since rabbits gnaw on wood. It absorbs water and urine, making good sanitation more difficult. If you do use wood, avoid treated wood because it may be harmful.
The basic cage used in most rabbitries is 30” deep x 36” long x 18” high. Most have rectangular sides (conventional style), but some have rounded tops (quonset style). Doors may be hinged at the top, sides or bottom.
The size of the cage varies with the size of the breed:
- Small breeds – 24”x24”x16” cage (ie. American Fuzzy Lop, Mini Lop or Rex, Dutch, or Netherland Dwarf)
- Medium breeds – 30”x30”x18” cage (ie. Rex, English or French Angora, or American Sable)
- Large breeds – 48”x30”x18” (ie. Flemish Giant, New Zealand, or Checkered Giant)
Materials needed
Conventional
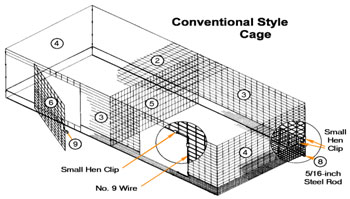
- 1 pc. 36x78-in wire
- 1 pc. 30x72-in wire
- 2 pc. 15x72-in wire
- 2 pc. 15x30-in wire
- 1 pc. 18x30-in wire
- 2 pc. 16x18-in wire
- 2 pc. 72-in sections of 5/16-in steel rod for floor 2 door latches
Quonset
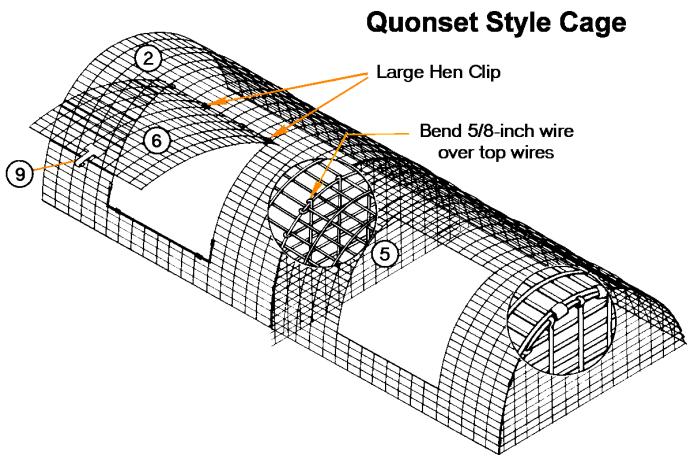
- 1 pc. 36x78-in wire
- 1 pc. 48x72-in wire
- 2 pc. 18x30-in wire
- 1 pc. 21x30-in wire
- 2 pc. 18x20-in wire
- 3 pc. No. 12 gal. wire
- 2 pc. 72-in sections of 5/16-in steel rod for floor 2 door latches
Fasteners: (common to both styles)
- 100 small hen-cage clips
- 25 large hen-cage clips
- 30 No. 101 hog rings
- 2 pc. 24-in No. 9 galvanized wire
The floor is made of 16-gauge welded wire with 1⁄2x1⁄2 or 1⁄2x1-inch grid openings.
Construction
These cages are most easily constructed in units of two cages. Lay out the floor first by removing a 3x3-inch section from each corner of the flooring. Bend up a 3-inch section along each side of the floor. Secure the floor sides together using small hen-cage clips to prevent young bunnies from falling from the cage. Attach the steel rods to the front and rear edges of the floor using hog rings. The partition and ends of the quonset cage are best shaped using a pattern. Allow a 5/8-inch section of the wires to extend beyond the pattern. Bend these wires around a No. 12 edging wire. Position the ends and partition on the floor and fasten them using small hen- cage clips. Attach the front and back sides of the conventional cages to the bent-up flooring. Do not fasten the front section to flooring in the area where the doors will be located. Fasten sides to the partition and ends. Lay the top of the quonset cages over the floor, ends and partition. Fasten to the front and rear of the flooring using small hen-cage clips spaced every five inches. Raise the center partition and fasten to the top. Repeat the process with each end section. Cut the door openings in the front side of each cage. Each opening should be 2- inches smaller than the doors in height and width. File all sharp protruding wires. Attach the doors using large hen cage clips as hinges. Attach the No. 9 wire around the door openings using the large-size clips. Install the door latch to complete the cage. The cages can be suspended from an overhead support using six strands of No. 12 galvanized wire. Attach a wire to each corner of the individual cages for proper support.
Detailed housing plans for rabbits can be found at the Mississippi State Extension link at https://extension.msstate.edu/sites/default/files/publications/building-construction-plans/6360.pdf
Basic Equipment
Water Containers – ceramic crocks, bottle-tube waterers and automatic waterers are all good for use in your rabbit cage. Key is that rabbits need clean, fresh water at all times.
Grain Containers – metal self feeder with a screened bottom. Can be purchased at livestock supply companies or your local grain store.
Nest Box – Provide a nest boxes for does before they give birth.
You can make ten kindling boxes from a single 4' x 8' sheet of 3/4" plywood. Be sure you have the means to transport a sheet of plywood home before starting this project! But, to make things easier, this cutting layout allows for the sheet to be cut into two 4' x 4' pieces.

You need the following tools: an electric rotary saw, a screwdriver or drill (recommended) with both screwdriver bit and regular bit just smaller than the screws you will use, a hammer, and pliers. A table saw is handy for making some of the cuts, but is not necessary. You will also need 120 screws (we used #10, 1-3/4", but other sizes will work), fence staples, and 1/2" x 1" (or 1/2" x 1/2") metal wire mesh. You may need some sandpaper if you have rough edges.
The next part goes a little easier with a partner. Set up two side pieces parallel to each other about ten inches apart with the solid 16" edge on the bottom. Place the back against the taller two edges with the 8" edge vertical and the 10" edge along the bottom and forming the top edge of the back . Using two screws per side, securely screw the back onto the sides. We found it was a lot easier to pre-drill before screwing the pieces together. (Note, if your pieces aren't cut exactly perfectly, don't worry, just make sure to line up the top edges so that the top piece fits--the mesh bottom is more forgiving.) Next, screw on the front piece to the shorter two edges of the nest box sides. Use two screws per side. Pre- drill for the screw holes. Now place the top on the higher edges of the sides and attach with four screws, pre-drilling for ease of assembly.
Bottom Mesh - Cut ten pieces of metal mesh 9-1/2" x 16". Use fence stables every three or four inches to attach the bottom to the nest box. Voila! You are finished.
Consideration
Does and bucks should not be kept in the same cage. The only time should be during breeding season. The doe is taken to the buck’s cage for mating. The doe is left long enough for the mating to occur. Remate the doe in 8 to 12 hours to increase litter size and conception rate. A mature buck may be mated to one or two does daily and serve a total of 10 to 20 does.
Note: Consider climate, conditions, use, and cost when deciding on your housing.
Note: Clean cages with one cup of chlorine bleach in a gallon of water. A clean cage and equipment help to prevent diseases.
Additional Information on Rabbit Housing
Mississippi State University Extension Service, Rabbit Housing Plans, http://extension.msstate.edu/sites/default/files/topic-files/small-animal/rab-6360b.pdf 2007.