Site Information to Gather When Calculating SMART Incentives
In 2018, the Massachusetts Department of Energy Resources (MA DOER) established the Solar Massachusetts Renewable Target (SMART) program, which regulates incentives associated with new solar photovoltaic (PV) development in the state. This document is part of a series of fact sheets designed to help farmers navigate the program.
Important Site Information to Collect
The following information is helpful to have on hand in order to estimate expected compensation rates for a proposed solar PV array design:
- Is your land eligible for enrollment in the Chapter 61A program, or has it been enrolled in the last 5 years? _____________________________________________________________________________
If you are not sure of your land’s status with regard to Chapter 61A, check with your town tax assessors’ office. They will have the information available for your property’s past tax history, and be able to help determine whether the property is currently eligible under the program. In order to receive Chapter 61A status, the property must be at least 5 acres in size and your land must be in agricultural or horticultural production for commercial purposes. Applications are typically due by mid-October to be included in the program the following year.
- Does your land have prime farmland soils, unique farmland soils, or soils of statewide importance? __________________________________________________________________________________
You can find soil definitions for your property on the MassMapper website (https://maps.massgis.digital.mass.gov/MassMapper/MassMapper.html) using the following process:
- On the right-hand side of the screen, select “Physical Resources,” and then “Soils.”
- Select “Prime Farmland Soils,” which will add it to the list in the bottom right portion of the screen.
- You can then find for your property by zooming in to the Massachusetts map, or entering a street address into the “Enter a location” box. To qualify as Important Agricultural Farmland, the land must be in one of the brownish-green colors identified as prime farmland soils in the box on the bottom right.
If you have difficulty with this process, please contact CEE for assistance.
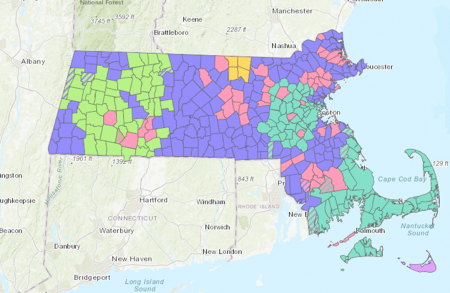
- What is your electricity service territory (local utility)? _______________________________________
If unsure, see the utility service territory map on page 5, or visit the MassGIS website.
- What is your annual on-farm electricity consumption? _______________________________________
Total your electricity bills for one year to estimate your annual electricity usage. This value should be given in kilowatt-hours, listed on your bill as kWh. This usage should include all metered electricity accounts associated with farm operations, but not the farm house, even if it is on the same property.
- What is your proposed system capacity (in kW AC)? __________________________________________
If your main objective is to supply annual on-farm electricity usage, divide your annual kWh usage (determined in question 5 above) by 1200. This will give you a rough estimate of the number of kW of installed capacity necessary to meet 100% of the annual on-farm electricity use.
- Is the end-use customer of the electricity generated by the solar PV array solely the farm, or will there be excess electricity over the course of the year? If there will be excess electricity, do you plan to assign that electricity (in whole or in part), to low-income housing, a community-shared project, or a public entity? ____________________
Note that low-income housing, community-shared projects, and public buildings do not have to be immediately adjacent to the solar array to be assigned electricity from it. Electricity can be assigned to other customers in the same utility service territory through virtual net metering.
- What type(s) of solar PV are you considering?
a. Building-mounted ______________
b. Canopy-mounted_______________
c. Ground-mounted_______________
d. Ground-mounted, with dual-use agriculture ________________________
- Would you be interested in incorporating on-site energy storage? ______________________________
Energy storage, typically in the form of batteries, adds value to the electric grid by allowing energy to be dispatched strategically to reduce peak demands. Batteries remain expensive, but the SMART program offers additional compensation to support battery storage. Farms with electric rates that include time-of-day rates or demand charges may also be able to use energy storage to reduce their electric bills.
If you are interested in installing a standard ground-mounted solar PV array with a large capacity (greater than 500 kW), you should have the following information on hand for the purpose of calculating compensation rates:
- Is the land being used for the array an eligible brownfield or landfill? _________________________
(See guideline: https://www.mass.gov/doc/smart-brownfields-guideline-final)
- Has the land being used for the array been previously developed with pavement or construction? _____________________________________________________________________________________
- Is your land zoned for industrial or commercial use? ________________________________________
Check with your local town clerk or planning department.
- Is your land in a solar overlay district as established by the town? ______________________________
Check with your local town clerk or planning department.
- Is the land characterized as BioMap2 Critical Natural Landscape or Priority Habitat?
See resource available from MassGIS: https://www.mass.gov/info-details/massgis-data-biomap-the-future-of-conservation
- What is the planned acreage of your array? ____________________________________________
Remember that 1 MW of traditional ground-mounted solar PV typically requires 6-8 acres of land in ideal circumstances.
General Information about Compensation Rates under the SMART Program
- A Base Compensation Rate is set based on the capacity of the system and the local utility service area. Over the course of the SMART program, the base rate declines by 4% for each “Capacity Block” that is filled in a given service area. You can check http://masmartsolar.com/ to determine which Capacity Block your site is in. Also review the Capacity Block Rate Guideline on the same website under Additional Resources, for additional details on compensation values.
- Small projects (≤ 25 kW) receive the highest Base Compensation Rates (in cents per kWh), but only for 10 years, compared to 20 years for larger projects.
- Projects of all sizes can receive additional incentives (cents per kWh) depending on the end-use customer for the electricity (e.g., low-income housing) and whether on-site energy storage is incorporated into the project.
- Larger projects (>25 kW) can receive additional incentives, depending on the location and whether the system is a fixed or tracking design. These incentives are also subject to a 4% decrease as each “tranche” is filled. See http://masmartsolar.com/ for more information.
- Qualifying as Category 1 Agricultural or Category 1 Non-Agricultural will lead to the highest compensation rates for larger projects (>25 kW).
- If your land is currently in the Chapter 61A program, has been in the past 5 years, or is on Prime Farmland Soils, it will qualify as Agricultural for the purposes of the SMART program. Projects on Agricultural land can qualify as Category 1 Agricultural if they 1) are building-mounted systems, 2) are sized to meet no more than 200% of on-farm demand, or 3) are dual-use systems up to 2 MW in capacity (or larger if they qualify for a waiver).
- If your land is not in the Chapter 61A program, has not been in the past 5 years, and is not on Prime Farmland Soils, it will be considered as Non-Agricultural land under the SMART program, regardless of whether farming is occurring on the land. Projects on Non-Agricultural land can qualify as Category 1 Non-Agricultural if they are 1) are building-mounted systems, 2) are canopy-mounted systems, or 3) are ground-mounted systems no more than 500 kW in capacity.
- If your proposed project is a ground-mounted system with a capacity between 500-5000 kW and it is in a solar overlay district, on previously developed land, or on an eligible brownfield or landfill, it can also qualify as Category 1 Non-Agricultural. Otherwise, if it is on land zoned for industrial or commercial use that has not been previously developed, it qualifies as Category 2. If it is on land that is not zoned for industrial or commercial use that has not been previously developed, it qualifies as Category 3, as long as it is not protected open space or a wetland resource area.
- Category 2 and 3 projects are subject to “subtractors” which reduce the compensation rate based on the acreage of land developed.
Service territory map courtesy of MassGIS
Calculating Compensation
A. Small systems (≤ 25 kW)
- Identify Base Compensation Rate ($ per kWh) from the table below. Note rate is higher if electricity is going to a low-income discounted rate customer. Values given are rounded to two decimal places. Actual base compensation rates are calculated to five decimal places. These values do not include the 4% decrease in base compensation rates that occurs as each capacity block is filled.
|
System type |
Massachusetts Electric d/b/a National Grid |
Nantucket Electric d/b/a National Grid |
NSTAR d/b/a Eversource Energy |
WMECO d/b/a Eversource Energy |
Fitchburg Gas & Electric d/b/a Unitil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Low-Income, system ≤25 kW |
0.36 |
0.39 |
0.39 |
0.33 |
0.36 |
|
System ≤25 kW |
0.31 |
0.34 |
0.34 |
0.29 |
0.31 |
- Determine Energy Storage Adder, if applicable. See the Energy Storage Guideline for this calculation.
- Add Base Compensation Rate and Energy Storage Adder, if applicable.
a. Base Rate ________________ (e.g., $0.31 per kWh)
b. Energy Storage Adder_______ (e.g., $0.06 per kWh)
c. Total Compensation Rate_________________ (e.g., $0.36 per kWh)
You will receive the estimated Total Compensation Rate ($ per kWh) calculated above for each kWh of energy your system generates.
B. Medium-to-large systems (>25 kW)
- Determine Base Compensation Rate ($ per kWh) from the table below, based on capacity of the array and service area. Note that values given are rounded to two decimal places. Actual base compensation rates are calculated to five decimal places. These values do not include the 4% decrease in base compensation rates that occurs as each capacity block is filled.
|
kW |
Massachusetts Electric d/b/a National Grid |
Nantucket Electric d/b/a National Grid |
NSTAR d/b/a Eversource Energy |
WMECO d/b/a Eversource Energy |
Fitchburg Gas & Electric d/b/a Unitil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
25 kW-250 kW |
0.23 |
0.26 |
0.26 |
0.21 |
0.23 |
|
250-500 kW |
0.19 |
0.21 |
0.21 |
0.18 |
0.19 |
|
500-1000 kW |
0.17 |
0.19 |
0.19 |
0.16 |
0.17 |
|
1000 kW plus |
0.16 |
0.17 |
0.17 |
0.14 |
0.16 |
- Determine Location Based Adder from the table below, if applicable. Note that you can only select one adder from this table. These values do not include the 4% decrease in adder rates that occurs as each “tranche” is filled.
|
Location Type |
Adder Value ($ per kWh) |
|---|---|
|
Building Mounted |
0.02 |
|
Brownfield |
0.03 |
|
Eligible Landfill |
0.04 |
|
Canopy Mounted* |
0.06 |
|
Dual-Use Agriculture** |
0.06 |
|
Floating |
0.03 |
*Only applicable to systems on Non-Agricultural land, or systems on Agricultural Land sized to meet no more than 200% of on-farm electricity consumption.
**Only applicable to systems on Agricultural land up to 2 MW in capacity, or larger systems which qualify for a waiver.
- Determine Off-taker Based Adder, if applicable. Note you can only select one. These values do not include the 4% decrease in adder rates that occurs as each “tranche” is filled.
|
Off-taker Type |
Adder Value ($ per kWh) |
|---|---|
|
Community Shared |
0.05 |
|
Low Income Property |
0.03 |
|
Low Income Community Shared |
0.06 |
|
Public Entity |
0.02 |
- Determine Energy Storage Adder, if applicable. See the Energy Storage Guideline for this calculation.
- Are you using a tracking system, rather than fixed panels? If yes, adder is $0.01 per kWh.
Is your proposed array a standard ground-mounted system between 500-5000 kW on land not previously developed? If so, unless it is in a solar overlay district or on a qualified landfill or brownfield, it will likely fall into Category 2 or Category 3, and you must apply a Greenfields Subtractor:
- Calculate Greenfields Subtractor, if applicable:
a. Category 2: If land is zoned for commercial or industrial development, multiply planned acreage by -0.0005: ___________________ (e.g., 10 acres * -0.0005 = -$0.005 per kWh)
b. Category 3: If land is not zoned for commercial or industrial development, multiply planned acreage by -0.001: _______________ (e.g., 10 acres * -0.001 = -$0.01 per kWh subtractor)
- Total items 1-6:
a. Base Compensation Rate ______ (e.g., $0.19 per kWh)
b. Location-Based Adder _________ (e.g., $0.06 per kWh)
c. Off-taker Based Adder _________ (e.g., $0.05 per kWh)
d. Energy Storage Adder__________ (e.g., $0.05 per kWh)
e. Tracking System Adder_________ (e.g., $0.01 per kWh)
f. Greenfields Subtractor_________ (e.g., -$0.01 per kWh)
g. Total Compensation Rate_____________________ (e.g., $0.35 per kWh)
- You will receive the estimated Total Compensation Rate calculated above for each kWh your system generates.