UMass Extension's Landscape Message is an educational newsletter intended to inform and guide Massachusetts Green Industry professionals in the management of our collective landscape. Detailed reports from scouts and Extension specialists on growing conditions, pest activity, and cultural practices for the management of woody ornamentals, trees, and turf are regular features. The following issue has been updated to provide timely management information and the latest regional news and environmental data.
Fall Wrap-Up Landscape Education Days
- Dec. 2 - Woody Ornamental Topics (3 pesticide contact hours for categories 29, 36 or Applicators License)
- Dec. 4 - Turf Topics (3 pesticide contact hours for categories 37 or Applicators License)
Join us via GoToWebinar for a review of the challenges and problems of the 2020 season. Attendees can choose to attend either the landscape or turf session, or the entire two-day program. Both will be held as live webinars from 8:30 am to 12:00 pm, with three topics on each day. For more details and registration info, go to https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/upcoming-events.
Registration is filling fast for our UMass Extension GREEN SCHOOL!
 Green School is going VIRTUAL for 2020! Classes will be Oct. 26 - Dec. 10.
Green School is going VIRTUAL for 2020! Classes will be Oct. 26 - Dec. 10.
This comprehensive 12-day certificate short course for Green Industry professionals is taught by UMass Extension specialists, University of Massachusetts faculty, and guest presenters.
Find the full schedule and registration info at http://ag.umass.edu/greenschool
For eligible employers in Massachusetts, the registration fee may be partially reimbursed (up to 50%) through the Massachusetts Workforce Training Fund Express Grant Program. Employers should submit an online application to the Express Grant program at least 4 weeks in advance of Green School's starting date. To find out if you qualify and to apply for benefits, go to http://workforcetrainingfund.org/apply/express-program/.
To read individual sections of the message, click on the section headings below to expand the content:
Scouting Information by Region
Environmental Data
The following data was collected on or about September 30, 2020. Total accumulated growing degree days (GDD) represent the heating units above a 50° F baseline temperature collected via our instruments for the 2020 calendar year. This information is intended for use as a guide for monitoring the developmental stages of pests in your location and planning management strategies accordingly.
|
MA Region/Location |
GDD |
Soil Temp |
Precipitation
|
Time/Date of Readings |
||
|
2-Week Gain |
2020 Total |
Sun |
Shade |
|||
|
CAPE |
208 |
2646.5 |
69 |
65 |
0.32 |
12:00 PM 09/30 |
|
SOUTHEAST |
169.5 |
2773.5 |
79 |
67 |
0.60 |
3:30 PM 09/30 |
|
NORTH SHORE |
171 |
2688 |
68 |
64 |
0.35 |
10:00 AM 9/30 |
|
EAST |
184 |
2943 |
71 |
67 |
1.03 |
5:00 PM 9/30 |
|
METRO |
135.5 |
2644.5 |
66 |
64 |
0.98 |
6:30 AM 9/30 |
|
CENTRAL |
161.5 |
2705.5 |
56 |
56 |
0.10 |
7:00 AM 9/30 |
|
PIONEER VALLEY |
145.5 |
2667 |
69 |
66 |
2.15 |
1:00 PM 9/30 |
|
BERKSHIRES |
131 |
2394.5 |
64 |
62 |
3.73 |
9:00 AM 9/30 |
|
AVERAGE |
163 |
2683 |
68 |
64 |
1.16 |
_ |
|
n/a = information not available |
||||||
This most recent map (9/29) shows about one third of our state in extreme drought and at least half in severe drought: https://droughtmonitor.unl.edu/CurrentMap/StateDroughtMonitor.aspx?MA
Water use restrictions and bans in effect in many towns as of 9/17. Check the MassDEP map: https://www.mass.gov/doc/water-use-restrictions-map/download
Regional Notes
Cape Cod Region (Barnstable)
General Conditions: The average temperature for the period from September 16 thru September 30 was 64˚F, with a high of 81˚F on 9/25 and a low of 44˚F on 9/19. From the 19th to the 22nd, temperatures were cool with highs barely reaching 60˚F. Since then, it has been significantly warmer with high temperatures in the mid to upper 70s and relative humidity following the same pattern - low during the cool days and high on the warmer days. Overall, the period has had mostly sunny days with some cloudy days recently. Precipitation during the period amounted to 0.32 inches; more had been forecast but actual amounts were very low. The rainfall total for June through Sept of 2020 has been only 4.42 inches, an even more severe drought compared to the last time severe drought conditions occurred – in 2016 - for which precipitation totals for the same period were 7.02 inches. Soil moisture conditions are very dry for both topsoil and subsoil. Half of the Cape is listed as in extreme drought while the other half is in a severe drought as of Sept. 19, according to the US Drought monitor: https://droughtmonitor.unl.edu/CurrentMap/StateDroughtMonitor.aspx?MA
Pests/Problems: The ongoing drought is the primary concern in the landscape at this time both in managed and unmanaged landscapes. The lack of soil moisture is causing wilting, scorch, foliar browning, premature defoliation, and plant failure. Maple trees are rapidly changing color and defoliating. The continual water stress on plants is likely to predispose them to secondary attacks by insects and fungi as well as winter injury. Insects or insect damage observed during the period include turpentine beetle damage to pitch pine and Norway spruce, pine tip moth damage to pitch pine and mugo pine, hemlock woolly adelgid and hemlock elongate scale on hemlock, lacebug damage to azalea and Andromeda, Hibiscus sawfly damage on hardy Hibiscus, two-spotted spider mite damage on many woody and herbaceous perennials, broadmite damage on Hydrangea paniculata, chilli thrip damage on Hydrangea macrophylla, sunflower moth damage to Echinacea, budworm damage on Petunia, white pine aphid causing branch dieback on Japanese white pine, daylily leafminer on daylily, Lecanium scale on oak, and white grub damage to turf. Disease symptoms or signs observed during the period include powdery mildew on just about everything, scorch on horsechestnut as a result of Guignardia leaf spot, cedar apple rust on crabapple, apple scab on crabapple, leaf spot of Rudbeckia, Cercospora leaf spot on bigleaf and oak leaf Hydrangea, leaf rust on blueberry and Aster yellows on goldenrod.
Southeast Region (Dighton)
General Conditions: Rain finally arrived on 9/30, although accompanying wind violently brought down tree limbs and leaves with it. The brutal and extended drought has both shortened the bloom of many plants and accelerated fall coloring of many others. These are times that test choices in landscaping, with many long-established plantings now wilted, defoliated and dead after towns had to ban outdoor watering for most of the summer. It will be next year before we will have a true assessment of the damage. I've noticed the following plants in flower: Nipponanthemum nipponicum (Montauk daisy), Symphyotrichum novae-angliae (New England aster), Solidago spp. (goldenrod), Aster pilosus (hairy white oldfield aster, frost aster), Eupatorium perfoliatum (common boneset), Rosa spp. (including ‘Knockout’ rose), Clematis paniculata (sweet autumn Clematis), Sedum spectabile (Sedum 'Autumn Joy', 'Black Jack'), Hosta spp. (plantain lily), Lagerstroemia spp. (crape myrtle), Oenothera laciniata (cutleaf evening primrose), Helianthus tuberosus (Jerusalem artichoke), and Linaria vulgaris (yellow toadflax).
Pests/Problems: Despite cooler temperatures, mosquitoes will continue to be a threat to workers in the landscape. Both West Nile virus and EEE infections have been reported. One of many fungal rust species was observed on turf and powdery mildew has been on the leaves of many plants.
North Shore (Beverly)
General Conditions: Along with the drought, the cooler weather of mid-September persisted in the first week of this two-week reporting period, but warmed up during the second week. The average daily temperature for this period was 62˚F, with the maximum temperature of 81˚F recorded on September 28 and the minimum temperature of 48˚F recorded on September 20 and 21. Temperatures during the first week of this period were mostly in the low 40s to low 60s and in the second week low to high 70s. A temperature of 80˚F and above was recorded on only one day during this period. Approximately 0.35 inches of rainfall were received at Long Hill, most of it occurring on the morning of September 30th. Woody plants seen in bloom include: seven-son flower (Heptacodium miconioides), Franklin tree (Franklinia alatamaha), Daphne (Daphne spp.) and blue mist shrub (Caryopteris x clandonensis). Herbaceous plants seen in bloom include: garden Phlox (Phlox paniculata), Japanese Anemone (Anemone x hybrida), hardy Begonia (Begonia grandis), cranesbill (Geranium spp.) and oxeye, false sunflower (Heliopsis helianthoides).
Pests/Problems: Magnolia scale continues to be observed on different Magnolia trees. Leaf tip and marginal necrosis was observed on Chinese Stewartia (Stewartia sinensis). Powdery mildew continues to be seen on some lilacs, beebalm (Monarda) and garden Phlox. Deer browsing was observed on young twigs of some trees and shrubs. Some shrubs and trees are showing signs of drought stress such as early fall color, leaf scorch and early leaf drop. Always use a mosquito repellent when working outdoors especially during dawn and dusk. Remember that ticks are still active and they will continue to be so whenever temperatures are above freezing. (Check out the archived FREE TickTalk with TickReport webinars link below in the Insect report section.)
East Region (Boston)
General Conditions: We had several fall-like days, with overnight temperatures dipping into the 40’s, leading up to the Autumnal Equinox on September 22. Beginning September 23, we returned to a week of summer-like conditions with temperatures in the mid to high 70’s. The streak of 17 consecutive days with no measurable precipitation was broken on September 28 when we received a negligible 0.05 inches of rain. We finally received 0.98 inches of beneficial rain on September 30. Fall color has begun most notably on birch, dogwood, honey locust and maple. Caryopteris x clandonensis (blue mist shrub), fall Asters, goldenrod, Montauk daisy and Russian sage continue to bloom. Pollinators can be found sleeping in the open flowers on cool mornings until they warm up and begin to forage.
Pests/Problems: Lack of precipitation continues to be a major concern in the landscape. As of September 28, we were having our 12th driest September since record keeping began in 1872. The 1.03 inches of welcome rain we received from the 28th through the 30th adjusted that to the 17th driest. Total rainfall for 2020 remains well below average and the landscape is visibly suffering from the extended drought conditions. High winds on the 30th brought down a significant amount of leaves and tree debris.
Metro West (Acton)
General Conditions: We welcomed fall during this two-week reporting period on the 22nd but one would never know it because of the warm summer like weather that we have been experiencing lately. With that being said, signs of the fall season are evident with foliage color change, shortened day lengths, some cooler temperatures and even light frosts on the mornings of the 19th, 20th and 21st. Glowing in the landscape are the red foliage on the sumacs, red maples, Virginia and Boston ivies, and the yellow foliage on the birches and honey locusts. September’s average rainfall is 3.77” and a total of 0.98” has been recorded for the month. October’s average monthly rainfall is 4.32”. Let’s hope to meet and exceed that average! Observed in some stage of bloom these past couple of weeks were the following woody plants: Buddleia spp. (butterfly-bush), Heptacodium miconioides (seven-son flower), Hibiscus syriacus (rose-of-Sharon), Potentilla fruiticosa (Potentilla), and Rosa 'Knockout' (‘Knockout’ family of roses). A woody vine in bloom is Clematis paniculata (sweet autumn Clematis). Contributing even more color and interest to the landscape are some flowering herbaceous plants including: Aster spp. (New England Aster, New York Aster, smooth Aster, white wood Aster), A. tataricus (Tatarian Aster), Caryopteris x clandonensis (blue mist shrub), Chelone lyonii (pink turtlehead), Echinacea purpurea (coneflower) and its many cultivars, Gentian spp., Hosta spp. (plantain lily), Kirengeshoma palmata (yellow wax bells), Patrinia gibbosa (Patrinia), Perovskia atriplicifolia (Russian sage), Phlox carolina (Carolina Phlox), P. paniculata (garden Phlox), Physostegia virginiana (obedient plant), Platycodon grandiflorus (balloon flower), Rudbeckia fulgida var. sullivantii 'Goldsturm' (black-eyed Susan), Sedum ‘Autumn Joy’, S. ‘Rosy Glow’ (stonecrops), and Solidago spp. (goldenrod). Adding even more color and interest to the landscape are plants heavy with fruit, seed, berries, and nuts. Examples are red fruits on Convallaria majalis (lily of the valley), Cornus florida (flowering dogwood), C. kousa (Kousa dogwood) and Ilex verticilata (winterberry). A variety of colors and sizes of fruits were seen on Callicarpa dichotoma (beautyberry), Cornus racemosa (gray dogwood), Crataegus spp. (hawthorn), Malus spp. (apple and crabapple), Rosa spp. (rose), Sorbus spp. (mountain ash), and Viburnum spp. Also noted were: attractive seed heads on ornamental grasses such as Chasmanthium latifolium (northern sea oats), Miscanthus spp. (maiden grass), Panicum virgatum (switchgrass), Pennisetum alopecuroides (fountain grass), seed pods on Catalpa and nuts on Carya spp. (hickory), Heptacodium miconioides (seven-son flower), Juglans spp. (walnut) and Quercus spp. (oak).
Pests/Problems: The dry weather pattern continued throughout this reporting period and as a result, on September 29nd, the United States Drought Monitor has declared most of Middlesex County in a severe drought with the southeast section even worse off in extreme drought. For five continuous months, beginning in May, recorded rainfall has not met its monthly average. Let’s hope that this pattern does not continue into October! Euonymus alatus (burning bush) is easy to detect now that it is in full color and one can see how it got its common name and how invasive it is. Another invasive plant displaying fall color and easier to detect climbing into the canopies of host trees is Celastrus orbiculatus (Oriental bittersweet).
Central Region (Boylston)
General Conditions: Fall came on rather quickly this reporting period. Our region experienced its first frosts on back to back evenings - September 20 and 21 - with temperatures dipping into the low 30’s, near freezing. We experienced our typical end of September weather swings, with temperatures reaching into the 80’s after a solid week of high temperatures in the 60’s. Fall foliage color and attractive fruit is abundant across the landscape. Unfortunately, heavy winds during the last night of the reporting period brought down much of the early tree color, but there is still plenty to enjoy for early October. Many of our native asters are in full bloom, including Symphyotrichum puniceum (purple-stemmed Aster) and S. novae-angliae (New England Aster), two important late season pollinator forage species.
Pests/Problems: Drought continues to be the single biggest landscape problem at this time. We received a scant 1.91 inches of precipitation for the entire month of September, far short of the monthly September average of about 4 inches. Many well-established landscape plants have required supplemental moisture to combat drought stress. The US Drought Monitor continues to show severe drought throughout central Massachusetts.
Pioneer Valley Region (Easthampton)
General Conditions: Autumn has officially arrived in the Pioneer Valley with the passing of the equinox. After only one storm of significance this month (9/10), we finally received soaking rainfall during the overnight hours of 9/29–30. The storm tracked quickly from the south and brought heavy rains and strong winds to the region. Gusts >35 mph were recorded at Barnes Airport in Westfield and numerous power outages were reported from downed trees and limbs. While over 2” was recorded in the Easthampton gauge, the rain is too little, too late for many landscape plants suffering from drought stress this season. Hopefully, it provides relief for some trees and shrubs and it certainly takes some strain off supplemental watering in the landscape. Even plants receiving irrigation suffered drought stress this season, due in part to a lack of proper watering (e.g. overhead sprinklers running for short intervals). Other factors included the incredible heat and competition with moisture-sucking turf. Still, it’s important to remind clients that supplemental watering is just that; supplemental to actual rain, which was scant for long periods this season. Future landscape designs should account for short term droughts during the summer and above-average temperatures, especially in full sun settings with well-drained soils. The most recent update to the U.S. Drought Monitor doesn’t account for the rainfall we just received and as a result, extreme drought (D3) categorization expanded into southern Hampden County. These classifications should likely improve in the next iteration on 10/8. Localized frosts on 9/21 and 9/22 really accelerated autumn leaf change and drop around the area. After a slow start to the foliage season, colors have really started shining brightly over this past week. Maple, birch, ash, Sassafras (such a deep orange), honeylocust, Euonymus, staghorn sumac and tupelo are coming into peak form as we enter October. Unfortunately, the strong winds from the recent storm sent many of those leaves to the ground. We also experienced a stretch from 9/19–22 with daily red flag warnings, indicating increased fire danger as humidity levels were low (maximum daily dew points were <45°F) and winds gusty. However, those conditions contrasted sharply with the days leading up the storm, when temperatures hovered >80°F from 9/25–28 and dew points peaked at 70° on 9/27 and 9/28. The humidity just prior to the storm on 9/29 was just plain swampy but the cool front has ushered in far more comfortable conditions.
Pests/Problems: Ensure transplanted conifers receive adequate irrigation through October, as the rain we just received will be quickly absorbed by bone dry soils. For deciduous trees and shrubs shedding foliage, water only to keep soils from completely drying out. Waterlogging soils when plants are going dormant can lead to problems. The warm, humid weather in late September resulted in a late season resurgence of biting mosquitoes. The cold night time temperatures in the long-term forecast should help to slow them down again. Allergy season roared back to life with pollen and spores abundant in the air during the windy days when humidity was low. Ragweed is the main culprit but a huge volume of fungal spores are also present in the air right now, despite the dry conditions. Start planning fall deer repellent applications. Many commercial grade repellents have a return interval of four to six weeks between treatments, depending on how much rain we receive. Around the valley, deer pressure seems highest in mid- to late winter for many landscape favorites (yew and arborvitae), but deterring these plant marauders now may help to eliminate a stop on the buffet later. For trees and shrubs with foliar disease problems, cleaning up fallen leaves helps to reduce disease pressure in the spring, when overwintering pathogens produce spores to initiate the disease cycle anew. For plants that aren’t shedding their foliage (e.g. Rhododendron and mountain laurel), pruning of badly infected leaves may be warranted to reduce the overwintering population.
Berkshire Region (Great Barrington)
General Conditions: Conditions of the past two weeks can be described in three words: drought, frost, and rain. Prior to this week, rainfall as recorded at Pittsfield Airport was 9.84 inches below normal for the year. As a result, many lawns were mottled with patches of green and brown turfgrass. Drought stress was also apparent on many deciduous trees as the transition to fall color began a little earlier than normal, as did leaf drop. The first frosts of the season occurred in many areas, especially in low-lying areas, on the mornings of Sept. 19 and 20. Here in West Stockbridge the low temperatures on those days were 30°F and 30°F. The same was true for North Adams, while the Richmond site registered 31°F on both days. Up slope sites throughout the County avoided these light frosts. Few sites escaped frost on the morning of Sept. 21. The first hard freeze was at this site in West Stockbridge where I recorded 27°F that morning and witnessed the demise of all tender vegetable crops as well as most annuals. Readings at other locales for that date were: 29°F in both North Adams and Richmond while Pittsfield Airport reported 30°F. Another frosty morning occurred on Sept. 22nd with readings of 30°F in West Stockbridge, and Pittsfield, 29°F in Richmond and 32°F in North Adams. The prolonged period of drought this year was abruptly ended when heavy rains fell on the evening of Sept. 28 and then from the afternoon of the 29th through the night and into the morning of Sept. 30th. Total rainfall in West Stockbridge for that period was 3.73 inches, in Richmond 3.39 inches, in Pittsfield 4.18 inches, in North Adams 3.65 inches, and in Lanesborough 4.8 inches. Needless to say, soil moisture is high and rain barrels are mostly full.
Pests/Problems: Perhaps because of the prolonged drought, pest and disease problems are low at this time. Leaf spots were responsible for some early leaf drop of late but were nowhere nearly as severe as last year. Deer tick populations and incidences of tick bites which were very high early in spring and summer dropped off dramatically over the past month, again likely due to the very dry conditions. Japanese beetle grubs are commonly found when digging in soil in gardens and turf. Wasps and yellowjackets are very active as are many biting gnats. Home invaders such as multicolored Asian ladybugs are making their move indoors. Browsing by deer, rabbits, chipmunks, woodchucks, and voles remained high through most of the scouting period, most likely due to the more luscious growth of ornamental plants in managed landscapes.
Regional Scouting Credits
- CAPE COD REGION - Russell Norton, Horticulture and Agriculture Educator with Cape Cod Cooperative Extension, reporting from Barnstable.
- SOUTHEAST REGION - Brian McMahon, Arborist, reporting from the Dighton area.
- NORTH SHORE REGION - Geoffrey Njue, Green Industry Specialist, UMass Extension, reporting from the Long Hill Reservation, Beverly.
- EAST REGION - Kit Ganshaw & Sue Pfeiffer, Horticulturists reporting from the Boston area.
- METRO WEST REGION – Julie Coop, Forester, Massachusetts Department of Conservation & Recreation, reporting from Acton.
- CENTRAL REGION - Mark Richardson, Director of Horticulture reporting from Tower Hill Botanic Garden, Boylston.
- PIONEER VALLEY REGION - Nick Brazee, Plant Pathologist, UMass Extension Plant Diagnostic Lab, temporarily reporting from Easthampton.
- BERKSHIRE REGION - Ron Kujawski, Horticultural Consultant, reporting from Great Barrington.
Woody Ornamentals
Diseases
Recent pests and pathogens of interest seen in the UMass Extension Plant Diagnostic Lab https://ag.umass.edu/services/plant-diagnostics-laboratory:
- Dieback of columnar juniper (Juniperus sp.) caused by cedar-quince rust and Botryosphaeria canker. Tree is approximately 25-years-old and has been present at the site for 20 years. Swollen galls/cankers were observed on the branches, due to infection by the cedar-quince rust pathogen, Gymnosporangium clavipes. Of all the Gymnosporangium species in the region, G. clavipes is the most destructive to both Juniperus and rosaceous hosts. These perennial cankers, which are not always obvious upon visual inspection, are sometimes colonized by opportunistic fungi. In this case, Botryosphaeria stevensii was detected causing additional stem dieback. The site is described as full sun with sandy loam soils and drip irrigation. Cedar-quince rust is nearly impossible to eradicate but efforts can be made to prune stems and branches that harbor the perennial cankers. Unfortunately, the galls often occur on primary branches and their removal would badly disfigure the tree.
- Stunted, thickened and curled leaves on a young (11-year-old) basswood (Tilia americana) due to paclobutrazol (Cambistat) treatment. The tree is situated with other Tilia in a residential setting with full sun and sandy soils. In previous years, the trees had exhibited symptoms of drought stress and were treated in 2019 to help increase fine root growth. The canopy was full and healthy this season, but the leaves were noticeably smaller and darker green compared to the other trees. A growth regulator, paclobutrazol treatment is known to result in undersized and thickened leaves on certain trees and shrubs, including Tilia.
- Leaf scorch and premature shedding in a white oak (Quercus alba) due to a jumping oak gall wasp (Neuroterus saltatorius) infestation and oak anthracnose (Apiognomonia errabunda). Well attended landscape tree on a college campus in full sun but also drought-prone soils. The tree is part of a stand of several mature white oaks that all appeared healthy, save for this tree. In early September, severe leaf scorching developed throughout the canopy. The submitted sample had a significant infestation of the jumping oak gall wasp. When populations are high, trees can suffer from widespread leaf blighting and premature shedding. Overall, this widespread gall wasp is not considered a major pest and prefers members of the white oak group. Submitted foliage was also harboring the oak anthracnose pathogen, which contributed to the symptoms.
- Stem and branch cankering of English walnut (Juglans regia) caused by Phomopsis and Juglanconis oblonga. Tree is approximately 35-years-old (12” dbh) and has been present at the site for nearly as long. For the past two years, branch dieback and early season defoliation have occurred, resulting in the loss of several large limbs. In spring of 2019, the tree received a deep root liquid fertilization, and was pruned in the fall. This autumn season, the root flare was exposed with an air spade. Phomopsis infections can result in chronic stem and small branch cankering that can be compounded by other stresses. Juglanconis is a newly erected genus for secondary cankering fungi that attack Juglans across the northern hemisphere. This particular species produces dark black masses of spores that can, at times, be visible on the bark of dead stems and is common in the region on butternuts (J. cinerea) declining from butternut canker.
- Volutella leaf and stem blight, caused by Pseudonectria buxi and P. foliicola, on boxwood (Buxus sp.). Plants are approximately five-years-old and have been present at the site for two years. They reside in full sun with drip irrigation in a gravel-topped bed between a stone driveway and stone patio. During the summer, plants exhibited browning leaves and black streaking on the stems. Pseudonectria was abundant on symptomatic stems and leaves and there was no evidence of the boxwood blight pathogen, Calonectria. One major difference in symptoms between Volutella blight and boxwood blight is that brown leaves are held in the canopy when Volutella blight is the culprit. When boxwood blight is the cause, leaves are readily shed from the canopy. Heat stress may be one contributing factor, given the setting.
 Excessive needle shedding and stem blight due to transplant shock and Diplodia blight on Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis). Mature tree of unknown age (17’ tall) that was transplanted in late July of this year. Site includes full sun and good loam soils. Older, interior needles are yellowing/reddening with the largest volume in the lower canopy. Conifers will often shed a large volume of needles during the first autumn season after transplanting. But some of the needles appeared brown, distinct from the color of naturally senescing needles. Submitted shoots and needles revealed that Diplodia sapinea was also present, causing a needle and shoot blight (see photo). Thorough pruning to remove all blighted shoots and removal (or covering) the dead needles should be enough to reduce disease severity. Watering will be critical in the years ahead to lessen the effects of transplant shock.
Excessive needle shedding and stem blight due to transplant shock and Diplodia blight on Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis). Mature tree of unknown age (17’ tall) that was transplanted in late July of this year. Site includes full sun and good loam soils. Older, interior needles are yellowing/reddening with the largest volume in the lower canopy. Conifers will often shed a large volume of needles during the first autumn season after transplanting. But some of the needles appeared brown, distinct from the color of naturally senescing needles. Submitted shoots and needles revealed that Diplodia sapinea was also present, causing a needle and shoot blight (see photo). Thorough pruning to remove all blighted shoots and removal (or covering) the dead needles should be enough to reduce disease severity. Watering will be critical in the years ahead to lessen the effects of transplant shock. Synthetic auxin herbicide exposure on Fraser fir (Abies fraseri). Landscape tree that is approximately 10-years-old and has been present on site for five years. The tree resides in full sun with drip irrigation. This spring, the tree began dropping needles and remaining needles were curled in a corkscrew pattern (see photo). Additionally, there was corky growth on isolated sections of the needles. No information was available on potential herbicide exposure but the symptoms are consistent with exposure to a synthetic auxin herbicide. These are often used to control broadleaf weeds in the landscape and unfortunately, exposure to non-target plants occurs on a regular basis.
Synthetic auxin herbicide exposure on Fraser fir (Abies fraseri). Landscape tree that is approximately 10-years-old and has been present on site for five years. The tree resides in full sun with drip irrigation. This spring, the tree began dropping needles and remaining needles were curled in a corkscrew pattern (see photo). Additionally, there was corky growth on isolated sections of the needles. No information was available on potential herbicide exposure but the symptoms are consistent with exposure to a synthetic auxin herbicide. These are often used to control broadleaf weeds in the landscape and unfortunately, exposure to non-target plants occurs on a regular basis.
Report by Nick Brazee, Plant Pathologist, UMass Extension Plant Diagnostic Lab, UMass Amherst.
Insects
Did you miss the live broadcasts of UMass Extension’s Invasive Insect Webinar Series? No problem! View the archived recordings of all seven webinars here:https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/education-events/invasive-insect-webinars
Did you miss my recent webinar with Urban Forestry Today and Dr. Rick Harper? No problem! View the archived recording of this webinar, along with many others, here: http://www.urbanforestrytoday.org/webcast-archives.html
Interested in learning more about insect identification and life cycles? Only have 3 minutes or less? Check out InsectXaminer! https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/education-events/insectxaminer
Insects and Other Arthropods of Public Health Concern:
- Mosquitoes: On July 3, 2020 the Massachusetts Department of Public Health announced that the eastern equine encephalitis (EEE) virus had been detected in mosquitoes in Massachusetts for the first time this year: https://www.mass.gov/news/state-public-health-officials-announce-seasons-first-eee-positive-mosquito-sample-0 . For more information about the first 2020 EEE detection and ways to protect yourself, visit the link above.
For current information, including searchable risk maps for both EEE and WNV in Massachusetts, visit:https://www.mass.gov/info-details/massachusetts-arbovirus-update
According to the Massachusetts Bureau of Infectious Disease and Laboratory Science and the Department of Public Health, there are at least 51 different species of mosquito found in Massachusetts. Mosquitoes belong to the Order Diptera (true flies) and the Family Culicidae (mosquitoes). As such, they undergo complete metamorphosis, and possess four major life stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Adult mosquitoes are the only stage that flies and many female mosquitoes only live for 2 weeks (although the life cycle and timing will depend upon the species). Only female mosquitoes bite to take a blood meal, and this is so they can make eggs. Mosquitoes need water to lay their eggs in, so they are often found in wet or damp locations and around plants. Different species prefer different habitats. It is possible to be bitten by a mosquito at any time of the day, and again timing depends upon the species. Many are particularly active from just before dusk, through the night, and until dawn. Mosquito bites are not only itchy and annoying, but they can be associated with greater health risks. Certain mosquitoes vector pathogens that cause diseases such as West Nile virus (WNV) and eastern equine encephalitis (EEE).
For more information about mosquitoes in Massachusetts, visit: https://www.mass.gov/service-details/mosquitoes-in-massachusetts
There are ways to protect yourself against mosquitoes, including wearing long-sleeved shirts and long pants, keeping mosquitoes outside by using tight-fitting window and door screens, and using insect repellents as directed. Products containing the active ingredients DEET, permethrin, IR3535, picaridin, and oil of lemon eucalyptus provide protection against mosquitoes.
For more information about mosquito repellents, visit: https://www.mass.gov/service-details/mosquitoes-in-massachusetts and https://www.cdc.gov/features/stopmosquitoes .
- Deer Tick/Blacklegged Tick: Check out the archived FREE TickTalk with TickReport webinars available here:https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/education-events/ticktalk-with-tickreport-webinars. Previous webinars including information about deer ticks and associated diseases, ticks and personal protection, and updates from the Laboratory of Medical Zoology are archived at the link above.
The next live webinar will be held on October 14, 2020 - Tick-borne Disease Surveillance in the US- Speaker: Dr. Ben Beard, Deputy Director, Division of Vector-Borne Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Dr. Rich welcomes Dr. Ben Beard to the TickTalk webinar. Dr. Beard will present the latest CDC findings on the burdens of tick-borne disease and public health trends. To register for the next TickTalk, visit:https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/education-events/ticktalk-with-tickreport-webinars
From October until roughly May, as long as daytime temperatures remain above freezing, adult male and female deer ticks (Ixodes scapularis) can be active, even in the winter. It is important to protect yourself against ticks and be especially vigilant for tiny, difficult to see nymphs. For images of all deer tick life stages, along with an outline of the diseases they carry, visit: http://www.tickencounter.org/tick_identification/deer_tick .
Anyone working in the yard and garden should be aware that there is the potential to encounter deer ticks. The deer tick or blacklegged tick can transmit Lyme disease, human babesiosis, human anaplasmosis, and other diseases. Preventative activities, such as daily tick checks, wearing appropriate clothing, and permethrin treatments for clothing (according to label instructions) can aid in reducing the risk that a tick will become attached to your body. If a tick cannot attach and feed, it will not transmit disease. For more information about personal protective measures, visit: http://www.tickencounter.org/prevention/protect_yourself .
Have you just removed an attached tick from yourself or a loved one with a pair of tweezers? If so, consider sending the tick to the UMass Laboratory of Medical Zoology to be tested for disease causing pathogens. To submit a tick to be tested, visit: https://www.tickreport.com/ and click on the blue “Order a TickReport” button. Results are typically available within 3 business days, or less. By the time you make an appointment with your physician following the tick attachment, you may have the results back from TickReport to bring to your physician to aid in a conversation about risk.
The UMass Laboratory of Medical Zoology does not give medical advice, nor are the results of their tests diagnostic of human disease. Transmission of a pathogen from the tick to you is dependent upon how long the tick had been feeding, and each pathogen has its own transmission time. TickReport is an excellent measure of exposure risk for the tick (or ticks) that you send in to be tested. Feel free to print out and share your TickReport with your healthcare provider.
- Wasps/Hornets: As frost arrives, annual wasp and hornet nests will cease in their activity and only fertilized females will overwinter in sheltered places.
Woody ornamental insect and non-insect arthropod pests to consider, a selected few:



 Spotted Lanternfly: (Lycorma delicatula, SLF) is not known to be established in Massachusetts landscapes at this time. However, due to the great ability of this insect to hitchhike using human-aided movement, it is important that we remain vigilant in Massachusetts and report any suspicious findings. Spotted lanternfly reports can be sent here:https://massnrc.org/pests/slfreport.aspx
Spotted Lanternfly: (Lycorma delicatula, SLF) is not known to be established in Massachusetts landscapes at this time. However, due to the great ability of this insect to hitchhike using human-aided movement, it is important that we remain vigilant in Massachusetts and report any suspicious findings. Spotted lanternfly reports can be sent here:https://massnrc.org/pests/slfreport.aspx
On September 25, 2020 the Massachusetts Department of Agricultural Resources (MDAR) urged Massachusetts residents to report signs of the invasive spotted lanternfly (Lycorma delicatula). They announced the finding of two dead specimens of SLF in Massachusetts communities, and are urging residents to report any sign of the invasive pest. The specimens were recovered in the towns of Milford and Norwood, and were brought into Massachusetts on materials shipped from Pennsylvania counties currently under a spotted lanternfly quarantine. Additionally, according to the September 25, 2020 press release, MDAR was recently notified that nursery stock with spotted lanternfly egg masses and adults may have been unintentionally imported and planted in several parts of Massachusetts.
MDAR is urging anyone who has received goods or materials, such as plants, landscaping materials, or outdoor furniture, from a state with a known SLF infestation to carefully check the materials, including any packaging, for signs of spotted lanternfly. Currently, there are known introductions of SLF in Connecticut, Delaware, Maryland, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and West Virginia. For more information about this most recent press release, please visit:https://www.mass.gov/news/state-agricultural-officials-urge-residents-to-report-signs-of-invasive-spotted-lanternfly .
Because no live lanternflies have, as of this press release, been found in Massachusetts, there is currently no evidence that SLF has become established in the Commonwealth. As a precaution, MDAR has planned surveys in the areas where the insects were found, to confirm that no live populations are present. While a dead lanternfly was previously found in the Boston area, in December of 2018, repeated surveys have found no further signs of SLF in that part of the state.
For a map of known, established populations of SLF as well as detections outside of these areas where individual finds of spotted lanternfly have occurred (but no infestations are present), visit: https://nysipm.cornell.edu/environment/invasive-species-exotic-pests/spotted-lanternfly/ This map depicts an individual detection of spotted lanternfly at a private residence in Boston, MA that was reported by the MA Department of Agricultural Resources on February 21, 2019. More information about this detection in Boston, where no established infestation was found, is provided here: https://www.mass.gov/news/state-agricultural-officials-urge-residents-to-check-plants-for-spotted-lanternfly
This insect is a member of the Order Hemiptera (true bugs, cicadas, hoppers, aphids, and others) and the Family Fulgoridae, also known as planthoppers. The spotted lanternfly is a non-native species first detected in the United States in Berks County, Pennsylvania and confirmed on September 22, 2014.
The spotted lanternfly is considered native to China, India, and Vietnam. It has been introduced as a non-native insect to South Korea and Japan, prior to its detection in the United States. In South Korea, it is considered invasive and a pest of grapes and peaches. The spotted lanternfly has been reported feeding on over 103 species of plants, according to new research (Barringer and Ciafré, 2020) and when including not only plants on which the insect feeds, but those that it will lay egg masses on, this number rises to 172. This includes, but is not limited to, the following: tree of heaven (Ailanthus altissima) (preferred host), apple (Malus spp.), plum, cherry, peach, apricot (Prunus spp.), grape (Vitis spp.), pine (Pinus spp.), pignut hickory (Carya glabra), Sassafras (Sassafras albidum), serviceberry (Amelanchier spp.), slippery elm (Ulmus rubra), tulip poplar (Liriodendron tulipifera), white ash (Fraxinus americana), willow (Salix spp.), American beech (Fagus grandifolia), American linden (Tilia americana), American sycamore (Platanus occidentalis), big-toothed aspen (Populus grandidentata), black birch (Betula lenta), black cherry (Prunus serotina), black gum (Nyssa sylvatica), black walnut (Juglans nigra), dogwood (Cornus spp.), Japanese snowbell (Styrax japonicus), maple (Acer spp.), oak (Quercus spp.), and paper birch (Betula papyrifera).
The adults and immatures of this species damage host plants by feeding on sap from stems, leaves, and the trunks of trees. In the springtime in Pennsylvania (late April - mid-May) nymphs (immatures) are found on smaller plants and vines and new growth of trees and shrubs. Third and fourth instar nymphs migrate to the tree of heaven and are observed feeding on trunks and branches. Trees may be found with sap weeping from the wounds caused by the insect’s feeding. The sugary secretions (excrement) created by this insect may coat the host plant, later leading to the growth of sooty mold. Insects such as wasps, hornets, bees, and ants may also be attracted to the sugary waste created by the lanternflies, or sap weeping from open wounds in the host plant. Host plants have been described as giving off a fermented odor when this insect is present.
Adults are present by the middle of July in Pennsylvania and begin laying eggs by late September and continue laying eggs through late November and even early December in that state. Adults may be found on the trunks of trees such as the tree of heaven or other host plants growing in close proximity to them. Egg masses of this insect are gray in color and look similar in some ways to gypsy moth egg masses.
Host plants, bricks, stone, lawn furniture, recreational vehicles, and other smooth surfaces can be inspected for egg masses. Egg masses laid on outdoor residential items such as those listed above may pose the greatest threat for spreading this insect via human aided movement.
For more information about the spotted lanternfly, visit this fact sheet: https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/fact-sheets/spotted-lanternfly .


 Asian Longhorned Beetle: (Anoplophora glabripennis, ALB) is a serious invasive insect that was first detected in Massachusetts in August of 2008. ALB was detected for the first time in South Carolina in 2020. Asian longhorned beetle eradication programs currently exist in Massachusetts, New York, and Ohio. A homeowner is responsible for finding, reporting, and making officials aware of the infestation in South Carolina. Great job!
Asian Longhorned Beetle: (Anoplophora glabripennis, ALB) is a serious invasive insect that was first detected in Massachusetts in August of 2008. ALB was detected for the first time in South Carolina in 2020. Asian longhorned beetle eradication programs currently exist in Massachusetts, New York, and Ohio. A homeowner is responsible for finding, reporting, and making officials aware of the infestation in South Carolina. Great job!
The U.S. Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) and the Clemson University’s Department of Plant Industry (DPI) are inspecting trees in Hollywood, South Carolina following the detection and identification of the Asian longhorned beetle (ALB).
On May 29, a homeowner in Hollywood, South Carolina contacted DPI to report they found a dead beetle on their property and suspected it was ALB. A DPI employee collected the insect the same day and conducted a preliminary survey of the trees on the property. Clemson’s Plant and Pest Diagnostic Clinic provided an initial identification of ALB, and on June 4, APHIS’ National Identification Services confirmed the insect. On June 11, APHIS and DPI inspectors confirmed that one tree on the property is infested, and a second infested tree was found on an adjacent property. For more information, visit: https://www.aphis.usda.gov/aphis/newsroom/stakeholder-info/sa_by_date/sa-2020/sa-06/alb-sc . A recently released “Draft Environmental Assessment for the Asian Longhorned Beetle Eradication Program in Charleston, Dorchester, and Colleton Counties in South Carolina” from the USDA-APHIS provides a map of the currently known infested trees in that location. For more information, visit:https://www.aphis.usda.gov/aphis/newsroom/federal-register-posts/sa_by_date/sa-2020/alb-draft-ea .
This is a good reminder for us to remain vigilant, and report any suspicious beetles or damage to trees, especially maples. Asian longhorned beetle infests 12 genera of trees, however maples are preferred hosts.
Look for signs of an ALB infestation which include perfectly round exit holes (about the size of a dime), shallow oval or round scars in the bark where a female has chewed an egg site, or sawdust-like frass (excrement) on the ground nearby host trees or caught in between branches. Be advised that other, native insects may create perfectly round exit holes or sawdust-like frass, which can be confused with signs of ALB activity.
The regulated area for Asian longhorned beetle is 110 miles2 encompassing Worcester, Shrewsbury, Boylston, West Boylston, and parts of Holden and Auburn. If you believe you have seen damage caused by this insect, such as exit holes or egg sites, on susceptible host trees like maple, please call the Asian Longhorned Beetle Eradication Program office in Worcester, MA at 508-852-8090 or toll free at 1-866-702-9938.
To report an Asian longhorned beetle find online or compare it to common insect look-alikes, visit: http://massnrc.org/pests/albreport.aspx or https://www.aphis.usda.gov/pests-diseases/alb/report .
More information can be found in the “Trouble Maker of the Month” section of July’s edition of Hort Notes:https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/newsletters/hort-notes/hort-notes-2020-vol-315
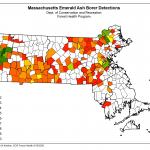


 Emerald Ash Borer: (Agrilus planipennis, EAB) As of September 18, 2020, the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation has confirmed a total of at least 139 communities in Massachusetts that have known populations of emerald ash borer, 40 of which have been found in 2020. An updated map of these locations across the state may be found here:https://ag.umass.edu/fact-sheets/emerald-ash-borer .
Emerald Ash Borer: (Agrilus planipennis, EAB) As of September 18, 2020, the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation has confirmed a total of at least 139 communities in Massachusetts that have known populations of emerald ash borer, 40 of which have been found in 2020. An updated map of these locations across the state may be found here:https://ag.umass.edu/fact-sheets/emerald-ash-borer .
This wood-boring beetle readily attacks ash (Fraxinus spp.) including white, green, and black ash and has also been found developing in white fringe tree (Chionanthus virginicus) and has been reported in cultivated olive (Olea europaea). Adult insects of this species will not be present at this time of year. Signs of an EAB infested tree may include (at this time) D-shaped exit holes in the bark (from adult emergence in previous years), “blonding” or lighter coloration of the ash bark from woodpecker feeding (chipping away of the bark as they search for larvae beneath), and serpentine galleries visible through splits in the bark, from larval feeding beneath. Positive identification of an EAB-infested tree may not be possible with these signs individually on their own.
For further information about this insect, please visit: https://ag.umass.edu/fact-sheets/emerald-ash-borer . If you believe you have located EAB-infested ash trees, particularly in an area of Massachusetts not identified on the map provided, please report here: http://massnrc.org/pests/pestreports.htm .
- Fall Home-Invading Insects: Various insects, such as ladybugs, boxelder bugs, seedbugs, and stink bugs will begin to seek overwintering shelters in warm places, such as homes, throughout the next couple of months. While such invaders do not cause any measurable structural damage, they can become a nuisance especially when they are present in large numbers. If you are not willing to share your home with such insects, now should be the time to repair torn window screens, repair gaps around windows and doors, and sure up any other gaps through which they might enter the home.
Concerned that you may have found an invasive insect or suspicious damage caused by one? Need to report a pest sighting? If so, please visit the Massachusetts Introduced Pests Outreach Project: http://massnrc.org/pests/pestreports.htm .
A note about Tick Awareness: deer ticks (Ixodes scapularis), the American dog tick (Dermacentor variabilis), and the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum) are all found throughout Massachusetts. Each can carry their own complement of diseases. Anyone working in tick habitats (wood-line areas, forested areas, and landscaped areas with ground cover) should check themselves regularly for ticks while practicing preventative measures. Have a tick and need it tested? Visit the web page of the UMass Laboratory of Medical Zoology (https://www.tickreport.com/ ) and click on the blue Order a TickReport button for more information.
Reported by Tawny Simisky, Extension Entomologist, UMass Extension Landscape, Nursery, & Urban Forestry Program
Landscape Practices
With practically all of Massachusetts in some degree of drought as of 9/29/20, according to the US Drought Monitor (https://droughtmonitor.unl.edu/CurrentMap/StateDroughtMonitor.aspx?MA), it is important to irrigate as efficiently as possible. The following tips will help ensure that irrigation applications are as beneficial as possible.
1. Be aware of, and follow, your local town or municipality water regulations. https://www.mass.gov/doc/water-use-restrictions-map/download
2. Don’t irrigate midday. Evaporation is greatest midday, which could mean that much of the water being applied is lost before it reaches plants! Wind also contributes to evaporation and can change irrigation spray patterns. Early morning and evening are the best times to irrigate.
3. Use drip irrigation or soaker hoses when possible. Overhead irrigation frequently results in watering non-plant surfaces and can result in water interception by plant canopies which can reduce the water that reaches the plants’ root systems.
4. Maintain your irrigation system. Check for leaks, broken spray heads, and perform an irrigation system audit to assure uniformity.
5. Use smart technology. Smart controllers can monitor soil moisture and use environmental conditions to adjust irrigation based on water being lost to evapotranspiration (evaporation and transpiration).
6. Water deeply, allowing water to soak into the ground. Irrigating slowly (via drip irrigation or a slow flow) is key to achieving infiltration vs. runoff. Newly installed plants will need more frequent irrigation until established, especially container grown plants that were produced in soilless substrates. Less frequent, deeper irrigation encourages good root growth which will help plants survive water stress.
7. Apply mulch to planting beds and in tree rings 2-4” deep. Please do not "volcano mulch": keep mulch away from the base of plants and trees. Mulch helps reduce evaporation, insulates plant roots, and can add organic matter to the soil.
8. [Editor's note: A general recommendation for fall mowing is to maintain a consistent mowing height throughout the fall with just a slight decrease for the last mowing if desired.]
9. Reduce the competition for water by controlling weeds.
10. Don’t apply fertilizer under drought conditions or to plants senescing in the fall. [Editor's note: With the exception of specialized situations (such as football fields that receive play late into the season, for example), turf experts generally discourage most lawn fertilization after September because it can interfere with the winter hardening process. This is true for most plants, not just turfgrass.]
11. Keep in mind that landscapes typically require one inch of water per week (including rainfall) but taper off in the fall as plants go dormant. Unsure of what your system or sprinkler is applying? You can use a rain gauge and see how much water is collected in a certain period of time (30 minutes for example). Use multiple rain gauges if possible to understand if you have good uniformity, or make sure the rain gauge is located in an “average area”.
Report by Mandy Bayer, Extension Assistant Professor of Sustainable Landscape Horticulture, UMass Stockbridge School of Agriculture
Additional Resources
Pesticide License Exams - The MA Dept. of Agricultural Resources (MDAR) is holding exams for new exam applicants. Space is still limited; to register, go to: https://www.mass.gov/pesticide-examination-and-licensing.
To receive immediate notification when the next Landscape Message update is posted, join our e-mail list or follow us on Facebook and Twitter.
For a complete listing of upcoming events, see our upcoming educational events https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/upcoming-events
For commercial growers of greenhouse crops and flowers - Check out UMass Extension's Greenhouse Update website
For professional turf managers - Check out Turf Management Updates
For home gardeners and garden retailers - Check out our home lawn and garden resources. UMass Extension also has a Twitter feed that provides timely, daily gardening tips, sunrise and sunset times to home gardeners at twitter.com/UMassGardenClip
Diagnostic Services
The UMass Plant Diagnostic Lab and the Soil & Plant Nutrient Testing Lab are open and taking samples (mail-in only please, walk-in samples cannot be accepted). Allow additional turnaround time as mail delivery and staffing have been altered due to the pandemic.
- Plant disease, insect pest and invasive plant/weed samples: go to https://ag.umass.edu/services/plant-diagnostics-laboratory for more details.
- Routine soil analysis and particle size analysis ONLY (no other types of analyses available at this time): go to https://ag.umass.edu/services/soil-plant-nutrient-testing-laboratory.
UMass Laboratory Diagnoses Landscape and Turf Problems - The UMass Extension Plant Diagnostic Lab is available to serve commercial landscape contractors, turf managers, arborists, nurseries and other green industry professionals. It provides woody plant and turf disease analysis, woody plant and turf insect identification, turfgrass identification, weed identification, and offers a report of pest management strategies that are research based, economically sound and environmentally appropriate for the situation. Accurate diagnosis for a turf or landscape problem can often eliminate or reduce the need for pesticide use. For sampling procedures, detailed submission instructions and a list of fees, see Plant Diagnostic Laboratory
Soil and Plant Nutrient Testing - The University of Massachusetts Soil and Plant Nutrient Testing Laboratory is located on the campus of The University of Massachusetts at Amherst. Testing services are available to all. The function of the Soil and Plant Nutrient Testing Laboratory is to provide test results and recommendations that lead to the wise and economical use of soils and soil amendments. For complete information, visit the UMass Soil and Plant Nutrient Testing Laboratory web site. Alternatively, call the lab at (413) 545-2311.
Ticks are active any time that temperatures are above freezing! Remember to take appropriate precautions when working and playing outdoors, and conduct daily tick checks. UMass tests ticks for the presence of Lyme disease and other disease pathogens. Learn more


