UMass Extension's Landscape Message is an educational newsletter intended to inform and guide Massachusetts Green Industry professionals in the management of our collective landscape. Detailed reports from scouts and Extension specialists on growing conditions, pest activity, and cultural practices for the management of woody ornamentals, trees, and turf are regular features. The following issue has been updated to provide timely management information and the latest regional news and environmental data.
The Landscape Message will be updated weekly in June. The next message will be posted on June 25. To receive immediate notification when the next Landscape Message update is posted, be sure to join our e-mail list
To read individual sections of the message, click on the section headings below to expand the content:
Scouting Information by Region
Environmental Data
The following data was collected on or about June 16, 2021. Total accumulated growing degree days (GDD) represent the heating units above a 50° F baseline temperature collected via regional NEWA stations for the 2021 calendar year. This information is intended for use as a guide for monitoring the developmental stages of pests in your location and planning management strategies accordingly.
|
MA Region/Location |
GDD |
Soil Temp |
Precipitation |
Time/Date of Readings |
||
|
1-Week Gain |
2021 Total |
Sun |
Shade |
|||
|
CAPE |
97.5 |
543.5 |
66 |
63 |
0.71 |
12:00 PM 6/16 |
|
SOUTHEAST |
98 |
596.5 |
81 |
61 |
0.65 |
3:00 PM 6/16 |
|
NORTH SHORE |
99 |
690.5 |
63 |
59 |
1.19 |
10:30 AM 6/16 |
|
EAST |
103.5 |
697 |
72 |
65 |
1.35 |
5:00 PM 6/16 |
|
METRO |
95.5 |
651.5 |
63 |
60 |
1.94 |
5:45 AM 6/16 |
|
CENTRAL |
100.5 |
676.5 |
70 |
68 |
1.18 |
4:00 PM 6/16 |
|
PIONEER VALLEY |
112.5 |
680.5 |
68 |
63 |
1.34 |
1:00 PM 6/16 |
|
BERKSHIRES |
92.5 |
520.5 |
66 |
60 |
1.02 |
8:00 AM 6/16 |
|
AVERAGE |
100 |
632 |
69 |
62 |
1.17 |
_ |
|
n/a = information not available |
||||||
As of 6/16, there is a "moderate drought" status for half of the Cape and "abnormally dry" conditions for the other half of the Cape and Islands: https://droughtmonitor.unl.edu/CurrentMap/StateDroughtMonitor.aspx?MA
Current municipal water restrictions are shown on this map: https://www.mass.gov/doc/water-use-restrictions-map/download
Phenology
| Indicator Plants - Stages of Flowering (BEGIN, BEGIN/FULL, FULL, FULL/END, END) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLANT NAME (Botanic/ Common) | CAPE | S.E. | N.S. | EAST | METRO W. | CENT. | P.V. | BERK. |
|
Rhus typhina (staghorn sumac) |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
|
Sambucus canadensis (American elderberry) |
Begin |
Begin/Full |
Begin/Full |
Full |
Full |
Begin/Full |
Full |
* |
|
Tilia cordata (littleleaf linden) |
Begin/Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
* |
|
Ligustrum spp. (privet) |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
* |
|
Catalpa speciosa (northern catalpa) |
Begin/Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Begin |
|
Kalmia latifolia (mountain laurel) |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Begin/Full |
|
Philadelphus spp. (mock orange) |
Full |
* |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
Full |
|
Cotinus coggygria (common smokebush) |
Full/End |
End |
Full/End |
End |
End |
End |
Full/End |
Full/End |
|
Syringa meyeri (Meyer lilac) |
End |
End |
End |
End |
End |
End |
End |
Full/End |
|
Rhododendron catawbiense (Catawba Rhododendron) |
End |
End |
End |
End |
End |
End |
End |
End |
| * = no activity to report/information not available | ||||||||
Regional Notes
Cape Cod Region (Barnstable)
General Conditions: The average temperature from June 9 – June 16 was 65˚F with a high of 85˚F on June 9 and a low of 43˚F on June 11. Most of the days during the period had lows in the upper 50s and highs in the 70s with an even mix of mostly sunny and mostly cloudy days. Rain fall recorded in Barnstable was about ¾ of an inch. Precipitation occurred on three days during the period but the most significant times were on June 12 and June 15. Soil moisture is short. Plants seen in bloom during the past week include Japanese tree lilac, yellowwood, kousa dogwood, witherod viburnum, arrowwood viburnum, sheep laurel, roses, ninebark, deutzia and Japanese spiraea. Herbaceous plants seen in bloom include peony, baptisia, catmint, meadowsweet, eryngium, daylily, kniphofia, bearded iris, Japanese iris, lupine, goat’s beard, foxglove, blood red geranium, lady’s mantle, oxeye daisy, fringed bleeding heart, lavender and amsonia.
Pests/Problems: Insect pests or damage observed during the period include oak shothole leafminer damage on white oak, lecanium scale adults with eggs underneath on white oak (lecanium scale populations range widely on the Cape at this time), ambrosia beetle on dogwood, turpentine beetle on pitch pine, viburnum leaf beetle damage to arrowwood viburnum (neither larvae or adults present at this time), rose slug sawfly damage to rose (no larvae present), columbine leafminer damage on columbine, winter moth damage on maple, azalea lacebug damage on azalea (nymphs and adults present), andromeda lacebug damage on andromeda, spruce spidermite damage on Alberta spruce, maple eyespot gall midge on red maple, and earwig damage to buddleia. Disease symptoms and signs seen over the period include white pine needle disease, needlecast on pitch pine, cercospora leaf spot on oak leaf hydrangea, sycamore anthracnose, and red thread on turf. Multiflora rose and black swallow-wort are in full bloom. Other weeds in bloom include narrowleaf plantain, yellowwood sorrel, curly dock, black medic, common groundsel, hawkweed, and white clover. More precipitation is needed. Rabbit problems persist. Dog ticks are abundant as are deer ticks.
Southeast Region (Dighton)
General Conditions: We've returned to more seasonable and comfortable June-like weather but there's still no relief from the dryness. Among the many plants flowering this past week I've noticed: Achillea (yarrow), Ailanthus altissima (tree of heaven), Allium (ornamental onion), Aruncus dioicus (goat's beard), Asclepias syriaca (common milkweed), Baptisia australis (false indigo), Catalpa speciosa (catawba), Clematis, Cornus kousa (Chinese dogwood), C. racemosa (grey dogwood), Coreopsis (tickseed), Daucus carota (Queen Anne's lace), Digitalis lutea (yellow foxglove), Echinacea purpurea (purple coneflower), Erigeron annuus (annual fleabane), Geranium sanguineum (bloody geranium), Hemerocallis fulva, (orange daylily), H. var. (daylily), Hosta var.(plantain lily), Hydrangea macrophylla, Hypericum perforatum (St. John's-wort), Ilex glabra (inkberry), Kalmia latifolia (mountain laurel), Lathyrus latifolius (perennial pea-vine), Leucanthemum vulgare (oxeye daisy), L. x superbum (shasta daisy), Ligustrum (privet), Lilium var. (true lilies), Linnaea amabilis (kolkwitzia, beautybush), Lonicera japonica (Japanese honeysuckle), Lotus corniculatus (bird's-foot trefoil), Lysimachia vulgaris (yellow loosestrife), Myosotis (forget-me-not), Nepta (catmint), Oenothera (evening primrose), Paeonia (peony), Papaver somniferum (breadseed poppy), Physocarpus (ninebark), Pilosella spp. (yellow hawkweed), Plantago lanceolata (buckhorn plantain), Potentilla spp.(cinquefoil), Rhododendron viscosa (swamp azalea), Rosa spp.(rose), Salvia nemorosa (sage), Sambucus canadensis (elderberry), Sedum stenopetalum (wormleaf stonecrop), Silene coronaria, Lychnis coronaria (rose campion), Solanum dulcamara (bitter nightshade), Spiraea japonica (Japanese spirea), Styrax japonicus (Japanese snow bell), Syringa reticulata (tree lilac), Tilia cordata (little-leaf linden), Trifolium pratense (red clover), T. repens (white clover), Verbascum thapsus (great mullein), Viburnum dentatum (arrowwood), V. plicatum (doublefile viburnum, Japanese snowball), and Viola tricolor (wild pansy).
Pests/Problems: Anthracnose (leaf spot) was seen on shagbark hickory. For more information on leaf spot on hickory, see: http://ipm.illinois.edu/diseases/series600/rpd621/index.html
North Shore (Beverly)
General Conditions: The weather was pleasantly cool and comfortable most of the days during this reporting period. We had scattered rain and thunderstorms that passed through during the weekend and brought some much needed precipitation. Approximately 1.19 inches of rainfall was recorded at Beverly airport during this period. Day temperatures were mostly in the mid-60s to low 70s and the night temperatures were mainly in the mid-50s. The average daily temperature was 64℉ with the maximum temperature of 81℉ recorded on June 13 and the minimum temperature of 49℉ recorded on June 11. Turf on lawns and landscapes is green and flourishing. Perennials and annual flowers are also flourishing and providing color in the landscapes. Woody plants seen in bloom include: Chinese dogwood (Cornus kousa), mock orange (Philadelphus spp.), mountain laurel (Kalmia latifolia), smoke bush (Cotinus coggygria) Japanese tree lilac (Syringa reticulata), Chinese tree lilac (Syringa pekinensis) and northern catalpa (Catalpa speciosa). Non-woody plants seen in bloom include: bush cinquefoil (Potentilla fruticosa), foam flower (Tiarella cordifolia), fetterbush (Leucothoe fontanesiana), peony (Paeonia spp.), cranesbill (Geranium spp.), Asian/ old fashioned bleeding heart (formerly Dicentra spectabilis, now Lamprocapnos spectabilis), Salvia spp., Rodger's flower/fingerleaf rodgersia (Rodgersia aesculifolia), goat’s beard (Aruncus dioicus), Japanese primrose (Primula japonica), water lily (Nymphaea odorata), columbine (Aquilegia spp.), sweet woodruff (Galium odoratum), Allium spp., ox-eye daisy (Leucanthemum vulgare) and annuals.
Pests/Problems: Apple scab was observed on crabapples. It is caused by the fungus (Venturia inaequalis) and common on susceptible apples and crabapples. It produces lesions that are most often seen on leaves, causing those leaves to yellow and drop prematurely. Removing fallen leaves can help minimize the disease. High pH iron deficiency interveinal chlorosis (yellowing between veins) was observed on blueberries and azaleas. You can correct iron deficiency by lowering the pH by using acidic fertilizer (ammonium sulphate) or applying elemental sulfur. Multiflora roses (Rosa multiflora), raspberry (Rubus rosifolius) and several other weeds are in full bloom. Make sure to control the weeds before they set seed. Remember mosquitoes and ticks are very active, so protect yourself with insect repellent when working outdoors, especially at dawn and at dusk.
East Region (Boston)
General Conditions: Daytime temperatures averaged 75˚F with a high of 87˚F on the ninth. Overnight lows averaged 58˚F with a low temperature of 48˚F on the 11th. We received precipitation on five of the previous seven days. The majority of which fell on the 12th and 14th; totaling 1.35 inches for the week and 1.47 thus far in June. We experienced isolated thunder showers on the 14th; several rain gauges in the area recorded over 2 inches of precipitation. Catalpa speciosa (northern catalpa) and Syringa reticulata (Japanese tree lilac) are in full bloom. Roses are adding a rainbow of color to the landscape. Cherries are ripening while peach and pear trees are forming fruit.
Pests/Problems: Weeds are thriving. Bittersweet nightshade (Solanum dulcamara), black swallowwort (Cynanchum louiseae) and multiflora rose (Multiflora rose) are flowering. Cottony Taxus scale (Pulvinaria floccifera) white masses can be seen on susceptible shrubs. Amelanchier spp. (shadbush) fruit is beginning to show signs of cedar-apple rust (Gymnosporangium juniperi) infection. The result of infection from the fungus Taphrina deformans (peach leaf curl) has been observed on peach trees. Aphids continue to be abundant throughout the landscape.
Metro West (Acton)
General Conditions: We welcome the first day of summer on Sunday, 6/20, with this week’s report! For the most part this past week, we’ve experienced pleasant yet wet days with moderate temperatures in the mid-70s and cool nights. Rain was recorded on 5 of the 7 days during this recording period, bringing our monthly total recorded precipitation to 1.9”. The historical monthly average rainfall for June is 3.93”. Observed in some stage of bloom this past week were the following woody plants: Buddleia spp. (butterfly-bush), Calycanthus ’Aphrodite’(Aphrodite allspice), Catalpa speciosa (northern catalpa), Cornus kousa (Kousa dogwood), Deutzia spp. (deutzia), Kalmia latifolia (mountain laurel), Ligustrum spp. (privet), Liriodendron tulipifera (tulip tree), Magnolia sieboldii (oyama magnolia), Philadelphus spp. (sweet mock orange), Physocarpus opulifolius (common ninebark), Potentilla fruiticosa (potentilla), Rhododendron viscosum (swamp azalea), Rosa gallica (French rose), R. glauca (shrub rose), R. 'Knockout' (knockout family of roses), Rosa rugosa (beach rose), Rosa spp. (rose), Sambucus canadensis (elderberry), Spiraea japonica 'Alpina' (daphne spirea), S. spp. (bridal wreath), Stewartia psuedocamellia (Japanese stewartia), Styrax japonicus (Japanese snow bell), Syringa reticulata (Japanese tree lilac), Tilia cordata (littleleaf linden) and Weigela florida (old fashioned weigela).
Woody vines observed in bloom include Clematis spp. (clematis), Hydrangea anomala petiolaris (climbing hydrangea), and Lonicera sempervirens (trumpet honeysuckle). Contributing even more color and interest to the landscape are some flowering herbaceous plants including: Achillea millefolium (yarrow), Allium schoenoprasum (chives), Amsonia hubrichtii (Arkansas blue star), Aruncus aethusifolius (dwarf goat’s beard), A. dioicus (goat’s beard), Asclepias syriaca (common milkweed), Baptisia australis (false blue indigo), Campanula takesimana ‘Elizabeth’ (bell flower), C. spp. (bell flower), Chrysogonum virginianum (green and gold), Clematis recta 'Purpurea' (clematis), Coreopsis spp. (tickseed), Dicentra eximia (fringed bleeding heart), Dictamnus albus (gas plant), Digitalis purpurea (foxglove), Filipendula spp. (meadow sweet), Geranium cantabrigiense 'Biokovo' and 'Cambridge' (hardy cranesbill), G. ‘Johnson’s Blue’ (cranesbill), G. macrorrhizum (bigroot geranium), G. sanguineum (bloody cranesbill), Hemerocallis 'Stella D'Oro' (daylily), Hemerocallis spp. (daylily), Hosta spp. (plantain lily), Iris sibirica (Siberian Iris), I. versicolor (blue flag iris), Leucanthemum x suberbum (shasta daisy), Lupinus 'Russell Woodfield Hybrids' (lupine), Lychnis coronaria (rose campion), Nepeta spp. (ornamental catmint), Paeonia spp. (peony), Penstemon digitalis 'Husker’s Red' (beardtongue), Phlox divaricata (Canadian phlox), Rodgersia pinnata (rodgersia), Salvia nemerosa (salvia), Sedum kamtschaticum (Russian stonecrop), Thymus praecox (thyme), Tradescantia spp. (spiderwort), and Veronica spp. (speedwell).
Pests/Problems: Branches are heavy and are hanging low with foliage and/or flowers that are also compounded with the weight of the rain. Observed in the landscape this past week was the dieback on many pines. Also, Rosa multiflora, an aggressive invasive thorny vine is in bloom and is very easy to detect with its abundant white flowers. It is seen throughout the landscape growing in, over, and amongst other trees and shrubs.
Central Region (Boylston)
General Conditions: Weather was just about perfect for much of the reporting period. The brutal heat of the previous week seems a distant memory. We’ve received plenty of precipitation lately, and garden plants and wild plants alike are enjoying the early summer warmth with adequate rainfall. We did receive our first thunderstorms of the season on Monday, rolling through the region without heavy downpours and high winds, but plenty of thunder and lightning. Rhododendrons are finishing up. Kousa dogwoods are in full bloom across the region and putting on a spectacular show. Cornus kousa (some sources have switched to calling this tree Benthamidia japonica, although that has not been widely adopted by most botanists and horticulturists) is a beautiful small flowering tree native to eastern Asia and Japan. It is cousin to our native Cornus florida (also sometimes called Benthamidia florida), but not subject to the foliar disease dogwood anthracnose that affects the native species. Blooming several weeks later than the native tree, kousa dogwood shares similar floral traits, including large (usually white) bracts that can be attractive for several weeks during the flowering period.
Pests/Problems: Azalea gall (Exobasidium vaccinii) was spotted on several native azalea species. This fungal pathogen causes large sea-green colored growths on leaves and branches of susceptible rhododendron species. Though normally not lethal, the galls can be unattractive, but can be easily managed by removing galls as they are spotted. Weed pressure is immense in the garden currently.
Pioneer Valley Region (Amherst)
General Conditions: We have reached the midpoint of June and the summer solstice is approaching fast as daylight reaches its zenith for the year. Since the way-too-early heat wave that gripped the region in early June, we have settled into seasonable conditions. Since 6/11, high temperatures have ranged from 64–81°F while low temperatures have spanned 51–61°F. Many areas of the valley recorded well over an inch of precipitation over the past week, primarily from a strong band of thunderstorms that swept through during the morning hours of 6/14. A rapid succession of lightning strikes and booming thunder accompanied a downpour of rainfall, with nearly 1.2” recorded in the Easthampton gauge. This significant rain event followed minor rainfall on the morning of 6/12. The cooler nights and rain sent soil temperatures back down after peaking over 70°F at the apex of the heat wave. Despite the recent rainfall, soil moisture levels are only adequate at this time, and supplemental irrigation is still required for many plants in full sun that were recently transplanted or are suffering from previous stress. The heavy rain dislodged many white pine pollen cones and we appear to be at the tail end of the tree pollen season, and what a season it was. Crickets and tree frogs are serenading in the early nighttime hours and lightning bugs are now beginning to emerge.
Pests/Problems: Interior and marginal leaf scorch from the intense heat earlier this month is visible on certain plants, such as rhododendron and Japanese maple, especially in nursery settings. Maple anthracnose can be readily observed on a range of native and non-native maples, pictured here on a mature red maple (Acer rubrum) in the landscape. The appearance of eastern white pines suffering needle blight has improved slightly since last week with the continued elongation of the current season’s needles. Most of the older, diseased needles were shed from the canopy and once the new growth is fully developed, trees will appear fuller. Needle blights rarely kill trees by themselves, but instead create a chronic stress that slowly starves conifers of nutrients and makes them more susceptible to drought and winter injury. Gypsy moth injury is scattered but mostly inconsequential this year in the Connecticut Valley. But some younger trees do show moderate levels of damage. This is the time of year when a large variety of defoliating, rolling, mining and webbing caterpillars can be found on hardwoods and conifers. The only way to detect some of these pests is by very closely scouting the canopy. Clearly, it’s ideal to intercept these pests before the symptoms of their damage becomes conspicuous. Spinosad works well in most situations in combating these pests but applications on plants in flower should be avoided to protect pollinating insects. For trees and shrubs producing new growth, this can be a good time to stimulate production with a liquid fertilizer. Results vary significantly by plant and location but in some cases, a dramatic improvement in vigor can be observed shortly after application. Rhododendrons and azaleas with pale green to chlorotic appearances can often be enhanced with liquid fertilization. As noted last week, Oriental beetles have emerged which means Japanese and Asiatic garden beetles will be close behind.
Berkshire Region (Great Barrington)
General Conditions: After a week of very warm (hot) conditions, the weather over the past week was very comfortable with daytime highs mostly in the mid-70s and nighttime temperatures in the mid-50s to low 60s. Since the beginning of the month, there has been little precipitation. Combined with some steady winds, these conditions left soils dry for the most part. Thus, the clouds and rain showers on June 14th were welcomed. The relatively dry conditions have slowed the growth of non-irrigated turf grass but there currently are no signs of stress or browning of the grass. Nevertheless, it is advisable to maintain a relatively high mowing height of 3 inches. This will encourage deeper root development and set up grass plants to better endure any prolonged periods of extreme heat and/or drought. As a side note, it seems that the best-looking lawns are the ones infiltrated with wild thyme though these lawns lack the darker green of turf grass. Despite the end of the bloom phase of most early spring flowering trees and shrubs, there remains an abundance of color in the landscape as herbaceous perennials have matured and set flowers.
Pests/Problems: Before this year, gypsy moth caterpillar infestations and related defoliation of woody plants had been of concern in the eastern part of the state. However, as the problem declined in the east, it is now of much concern here in Berkshire County as there has been a proliferation of the caterpillar in woodlands and managed landscapes. The numbers are so great in woodlands that the caterpillar droppings from infested trees sound like rain drops. The size of the caterpillars is quite variable, indicating various instar stages. Though many are in the last instar stages, there is the occasional sight of ballooning caterpillars. These are the young caterpillars, not yet feeding, that dangle from silken threads waiting to be wind-blown to their ultimate feeding destination. (See the gypsy moth entry in the Insect Report below for photographs from Great Barrington.) As for other pests: elongate hemlock scale is now in the crawler stage; mines created by birch leaf miner are evident though few in number right now; imported willow leaf beetle was found in egg, larva, and adult stages on a single plant. Also observed were lily leaf beetle adults, euonymus scale, and woolly beech scale. The honey dew created by the latter pest is now covering the foliage of beech, mostly copper beech, and it won’t be long before sooty mold will be coating the sticky leaves. Plant diseases have been few thus far. Only the most common foliar diseases have been observed. These include apple scab, cedar-apple rust, and black spot on roses. At one site, a portion of a ground cover of Vinca minor growing beneath a deciduous tree succumbed to a dense layer of last fall’s leaves which had accumulated over the ground cover. That’s just a reminder that a heavy cover of autumn leaves can be damaging to ground covers.
Regional Scouting Credits
- CAPE COD REGION - Russell Norton, Horticulture and Agriculture Educator with Cape Cod Cooperative Extension, reporting from Barnstable.
- SOUTHEAST REGION - Brian McMahon, Arborist, reporting from the Dighton area.
- NORTH SHORE REGION - Geoffrey Njue, Green Industry Specialist, UMass Extension, reporting from the Long Hill Reservation, Beverly.
- EAST REGION - Kit Ganshaw & Sue Pfeiffer, Horticulturists reporting from the Boston area.
- METRO WEST REGION – Julie Coop, Forester, Massachusetts Department of Conservation & Recreation, reporting from Acton.
- CENTRAL REGION - Mark Richardson, Director of Horticulture reporting from Tower Hill Botanic Garden, Boylston.
- PIONEER VALLEY REGION - Nick Brazee, Plant Pathologist, UMass Extension Plant Diagnostic Lab, reporting from Amherst.
- BERKSHIRE REGION - Ron Kujawski, Horticultural Consultant, reporting from Great Barrington.
Woody Ornamentals
Diseases
Recent pests and pathogens of interest seen in the UMass Extension Plant Diagnostic Lab https://ag.umass.edu/services/plant-diagnostics-laboratory:
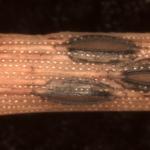
 Lophodermium needle cast of pitch pine (Pinus rigida) caused by Lophodermium seditosum. Yellowing and browning needles on a large number of forest pitch pines was reported in Plymouth and other areas of the south shore. This sample originated from a tree in Myles Standish State Forest. Outbreaks of Lophodermium needle cast are not common on forest trees, but hard pines like P. rigida can be severely impacted at times. More often, the disease is a problem on young pines at Christmas tree farms. The fungus sporulates from late summer to late fall and infects the current season’s needles. They become symptomatic the following spring, becoming most conspicuous in late April to early May. Dead needles can remain in the canopy, allowing inoculum to persist close to healthy needles. Abundant rainfall from August to November aids in spore dispersal and infection. While August and September were very dry in 2020, rainfall was plentiful in October and November, providing the necessary conditions for disease development.
Lophodermium needle cast of pitch pine (Pinus rigida) caused by Lophodermium seditosum. Yellowing and browning needles on a large number of forest pitch pines was reported in Plymouth and other areas of the south shore. This sample originated from a tree in Myles Standish State Forest. Outbreaks of Lophodermium needle cast are not common on forest trees, but hard pines like P. rigida can be severely impacted at times. More often, the disease is a problem on young pines at Christmas tree farms. The fungus sporulates from late summer to late fall and infects the current season’s needles. They become symptomatic the following spring, becoming most conspicuous in late April to early May. Dead needles can remain in the canopy, allowing inoculum to persist close to healthy needles. Abundant rainfall from August to November aids in spore dispersal and infection. While August and September were very dry in 2020, rainfall was plentiful in October and November, providing the necessary conditions for disease development.- Canopy dieback of blue spruce (Picea pungens) due to several pests and pathogens. Diseases detected included Stigmina needle cast (Stigmina lautii) and Phomopsis stem cankering (Phomopsis sp.). Insect pests found included the spruce spider mite (Oligonychus ununguis), spruce bud scale (Physokermes piceae) and the Cooley spruce gall adelgid (Adelges cooleyi). This assemblage of pathogens and pests is common on declining blue spruce in the landscape. The tree is mature, approximately 45- to 50-years-old, and resides in a residential setting with full sun. Branch dieback started in the lower canopy and has since spread upwards over the course of many years. The lower canopy branches, spanning 8-10’ from the ground, have been removed to reduce inoculum, improve the appearance and increase air flow. A large rhododendron that was growing into the tree and a volunteer tree were also removed. As the tree and surrounding plants matured, light became less available in the lower canopy and pests and pathogen activity increased. Mulch will be applied around the tree to help improve water retention in the soil and cover discarded needles that may harbor Stigmina.
- Sudden dieback of blue holly (Ilex × meserveae) caused by transplant shock and Botryosphaeria cankering (Botryosphaeria sp.). The plant is approximately 15-years-old and was transplanted in early May of this year. Two weeks after transplanting, symptoms of severe dieback developed. The plant arrived at the site with a large root ball but a significant portion was removed prior to establishment. It was placed in a shaded setting with clay-based soils and no supplemental irrigation. Submitted stems were blackened and clearly suffering from a cankering disease. Botryosphaeria is common on recently transplanted Ilex species, which often have dense canopies and thin bark, which help to facilitate disease development.
- Infestation of the oak shothole leafminer (Japanagromyza viridula) and stem cankering caused by Diplodia corticola in the canopy of a red oak (Quercus rubra). The tree is approximately 80- to 90-years-old and resides on the edge of a wooded property adjacent to a long driveway. This spring, as the tree was leafing out, half of the canopy appeared normal while the other half had undersized, stunted leaves and scattered small branch dieback. In 2019, the region experienced a major outbreak of the oak shothole leafminer and infested trees appeared to leaf out later in comparison to uninfested trees. This was a surprising outbreak since the leafminer had been uncommon to rare for decades in New England. While occurrence of the leafminer was drastically lower in 2020, populations seem to be higher in 2021. Diplodia corticola is very adept at colonizing stressed oaks and furthering the decline by creating girdling and eruptive stem cankers on small stems and branches.
- Canopy dieback of Japanese maple (Acer palmatum) caused by Phomopsis. The tree is roughly 20-years-old and resides in a shaded garden with drip irrigation in sandy-loam soils. In previous years, the tree was overwatered but unfortunately, was under-watered during last year’s drought and extreme heat. Last spring and also again this year, leaves emerge and then quickly die on scattered branches that are up to 1” in diameter.
 Construction damage to mature pin oak (Quercus palustris) on the UMass campus. The tree was planted to commemorate the class 1919 and resides on the eastern side of campus. While not particularly large (70’ tall with a dbh of 32”), the tree has performed well and inhabits an age class (>100-years-old) not well represented across campus. A large trench was dug in early June within the drip line to install new electrical conduit for an electric car-charging station. Root severing and compaction occurred when the trench was dug and then backfilled by an excavator that operated close to the trunk. UMass Landscape Services staff, which manage and protect trees on campus, were not consulted prior to the construction. As such, simple modifications to the plan that could have installed the conduit while minimizing the root damage were not possible. This case continues a trend of disregard for mature trees on the UMass campus, which suffer from frequent and avoidable construction-related injuries that contribute significantly to their decline and death.
Construction damage to mature pin oak (Quercus palustris) on the UMass campus. The tree was planted to commemorate the class 1919 and resides on the eastern side of campus. While not particularly large (70’ tall with a dbh of 32”), the tree has performed well and inhabits an age class (>100-years-old) not well represented across campus. A large trench was dug in early June within the drip line to install new electrical conduit for an electric car-charging station. Root severing and compaction occurred when the trench was dug and then backfilled by an excavator that operated close to the trunk. UMass Landscape Services staff, which manage and protect trees on campus, were not consulted prior to the construction. As such, simple modifications to the plan that could have installed the conduit while minimizing the root damage were not possible. This case continues a trend of disregard for mature trees on the UMass campus, which suffer from frequent and avoidable construction-related injuries that contribute significantly to their decline and death.
Report by Nick Brazee, Plant Pathologist, UMass Extension Plant Diagnostic Lab, UMass Amherst.
Insects
Insects and Other Arthropods of Medical Importance:

 American Dog Tick: Anecdotally, Dermacentor variabilis adults are prevalent in certain locations of Massachusetts at this time. Reports from Cape Cod of adult dog ticks crawling on the siding of homes have been noted. Photographic evidence of adult dog ticks crawling up metal objects leaning against a home located in a heavily wooded area of Berkshire County, MA have also been reported recently (5/9/2021). The images shown here are adult stage dog ticks removed from a dog following a roadside walk in Hampshire County on both 5/6/21 (4 ticks removed) and 5/7/21 (3 ticks removed). Looking for more updates? Check out UMass Extension’s Tick Check with Blake Dinius, Plymouth County Extension Service and Larry Dapsis, Cape Cod Cooperative Extension: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gryCv8qB1qw .
American Dog Tick: Anecdotally, Dermacentor variabilis adults are prevalent in certain locations of Massachusetts at this time. Reports from Cape Cod of adult dog ticks crawling on the siding of homes have been noted. Photographic evidence of adult dog ticks crawling up metal objects leaning against a home located in a heavily wooded area of Berkshire County, MA have also been reported recently (5/9/2021). The images shown here are adult stage dog ticks removed from a dog following a roadside walk in Hampshire County on both 5/6/21 (4 ticks removed) and 5/7/21 (3 ticks removed). Looking for more updates? Check out UMass Extension’s Tick Check with Blake Dinius, Plymouth County Extension Service and Larry Dapsis, Cape Cod Cooperative Extension: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gryCv8qB1qw .
The American dog tick is found throughout most of North America. It may be encountered in forest edges, fields, along walkways and roadways, sidewalks, and trails. Adult stage ticks may be found on raccoons, skunks, cats, dogs, and other medium-sized hosts. Larvae and nymphs can be found on mice, voles, rats, and chipmunks. Adult males and females are active between April and early-August. Both adult males and females will feed, including on people. Nymphs and larvae of this species rarely attach to people or their pets. This species of tick can transmit lesser-known diseases such as Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (not frequently infecting humans, according to CDC reports) and Tularemia (rarely infecting humans, according to CDC reports). For more information about the American dog tick, visit: https://web.uri.edu/tickencounter/species/dog-tick/ .
- Deer Tick/Blacklegged Tick: Check out the archived FREE TickTalk with TickReport webinars available here: https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/education-events/webinars .
*Ixodes scapularis - We are now entering the time of year when deer tick larvae and nymphs are frequently encountered. Larvae may be encountered in April, but in some locations may peak in their activity in August, while still being encountered through November. Nymphs are encountered from April through July, peaking in June. Nymphs are again present in October and November. For images of all deer tick life stages, along with an outline of the diseases they carry, and their timing of activity, visit: http://www.tickencounter.org/tick_identification/deer_tick .
Anyone working in the yard and garden should be aware that there is the potential to encounter deer ticks. The deer tick or blacklegged tick can transmit Lyme disease, human babesiosis, human anaplasmosis, and other diseases. Preventative activities, such as daily tick checks, wearing appropriate clothing, and permethrin treatments for clothing (according to label instructions) can aid in reducing the risk that a tick will become attached to your body. If a tick cannot attach and feed, it will not transmit disease. For more information about personal protective measures, visit: http://www.tickencounter.org/prevention/protect_yourself .
The Center for Agriculture, Food, and the Environment provides a list of potential tick identification and testing resources here: https://ag.umass.edu/resources/tick-testing-resources .
*Note that deer ticks (Ixodes scapularis) are not the only disease-causing tick species found in Massachusetts. The American dog tick (Dermacentor variabilis) and the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum) are also found throughout MA. Each can carry their own complement of diseases, including others not mentioned above. Anyone working or playing in tick habitats (wood-line areas, forested areas, and landscaped areas with ground cover) should check themselves regularly for ticks while practicing preventative measures.
- Mosquitoes: According to the Massachusetts Bureau of Infectious Disease and Laboratory Science and the Department of Public Health, there are at least 51 different species of mosquito found in Massachusetts. Mosquitoes belong to the Order Diptera (true flies) and the Family Culicidae (mosquitoes). As such, they undergo complete metamorphosis, and possess four major life stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Adult mosquitoes are the only stage that flies and many female mosquitoes only live for 2 weeks (although the life cycle and timing will depend upon the species). Only female mosquitoes bite to take a blood meal, and this is so they can make eggs. Mosquitoes need water to lay their eggs in, so they are often found in wet or damp locations and around plants. Different species prefer different habitats. It is possible to be bitten by a mosquito at any time of the day, and again timing depends upon the species. Many are particularly active from just before dusk, through the night, and until dawn. Mosquito bites are not only itchy and annoying, but they can be associated with greater health risks. Certain mosquitoes vector pathogens that cause diseases such as West Nile virus (WNV) and eastern equine encephalitis (EEE).
For more information about mosquitoes in Massachusetts, visit: https://www.mass.gov/service-details/mosquitoes-in-massachusetts .
There are ways to protect yourself against mosquitoes, including wearing long-sleeved shirts and long pants, keeping mosquitoes outside by using tight-fitting window and door screens, and using insect repellents as directed. Products containing the active ingredients DEET, permethrin, IR3535, picaridin, and oil of lemon eucalyptus provide protection against mosquitoes.
For more information about mosquito repellents, visit: https://www.mass.gov/service-details/mosquito-repellents and https://www.cdc.gov/mosquitoes/mosquito-bites/prevent-mosquito-bites.html .

 Wasps/Hornets: Many wasps are predators of other arthropods, including pest insects such as certain caterpillars that feed on trees and shrubs. Adult wasps hunt prey and bring it back to their nest where young are being reared, as food for the immature wasps. A common such example are the paper wasps (Polistes spp.) who rear their young on chewed up insects. They may be seen searching plants for caterpillars and other soft-bodied larvae to feed their young. Paper wasps can sting, and will defend their nests, which are open-celled paper nests that are not covered with a papery “envelope”. These open-celled nests may be seen hanging from eaves or other outdoor building structures. Aerial yellow jackets and hornets create large aerial nests that are covered with a papery shell or “envelope”. Common yellow jacket species include those in the genus Vespula. Dolichovespula maculata is commonly known as the baldfaced hornet, although it is not a true hornet. The European hornet (Vespa crabro) is three times the size of a yellow jacket and may be confused for the Asian giant hornet (Vespa mandarinia). The European hornet is known to Massachusetts, but the Asian giant hornet is not. If you are concerned that you have found or photographed an Asian giant hornet, please report it here: https://massnrc.org/pests/report.aspx . Paper wasps and aerial yellowjackets overwinter as fertilized females (queens) and a single female produces a new nest annually in the late spring. Nests are abandoned at the end of the season. Queens start new nests, lay eggs, and rear new wasps to assist in colony/nest development.Some people are allergic to stinging insects, so care should be taken around wasp/hornet nests. Unlike the European honeybee (Apis mellifera), wasps and hornets do not have barbed stingers, and therefore can sting repeatedly when defending their nests. It is best to avoid their nests, and if that cannot be done and assistance is needed to remove them, consult a professional.
Wasps/Hornets: Many wasps are predators of other arthropods, including pest insects such as certain caterpillars that feed on trees and shrubs. Adult wasps hunt prey and bring it back to their nest where young are being reared, as food for the immature wasps. A common such example are the paper wasps (Polistes spp.) who rear their young on chewed up insects. They may be seen searching plants for caterpillars and other soft-bodied larvae to feed their young. Paper wasps can sting, and will defend their nests, which are open-celled paper nests that are not covered with a papery “envelope”. These open-celled nests may be seen hanging from eaves or other outdoor building structures. Aerial yellow jackets and hornets create large aerial nests that are covered with a papery shell or “envelope”. Common yellow jacket species include those in the genus Vespula. Dolichovespula maculata is commonly known as the baldfaced hornet, although it is not a true hornet. The European hornet (Vespa crabro) is three times the size of a yellow jacket and may be confused for the Asian giant hornet (Vespa mandarinia). The European hornet is known to Massachusetts, but the Asian giant hornet is not. If you are concerned that you have found or photographed an Asian giant hornet, please report it here: https://massnrc.org/pests/report.aspx . Paper wasps and aerial yellowjackets overwinter as fertilized females (queens) and a single female produces a new nest annually in the late spring. Nests are abandoned at the end of the season. Queens start new nests, lay eggs, and rear new wasps to assist in colony/nest development.Some people are allergic to stinging insects, so care should be taken around wasp/hornet nests. Unlike the European honeybee (Apis mellifera), wasps and hornets do not have barbed stingers, and therefore can sting repeatedly when defending their nests. It is best to avoid their nests, and if that cannot be done and assistance is needed to remove them, consult a professional.
Woody ornamental insect and non-insect arthropod pests to consider, a selected few:
Invasive Insects & Other Organisms Update:
 Spotted Lanternfly: (Lycorma delicatula, SLF) is not known to be established in Massachusetts landscapes at this time. However, due to the great ability of this insect to hitchhike using human-aided movement, it is important that we remain vigilant in Massachusetts and report any suspicious findings. Spotted lanternfly reports can be sent here: https://massnrc.org/pests/slfreport.aspx .
Spotted Lanternfly: (Lycorma delicatula, SLF) is not known to be established in Massachusetts landscapes at this time. However, due to the great ability of this insect to hitchhike using human-aided movement, it is important that we remain vigilant in Massachusetts and report any suspicious findings. Spotted lanternfly reports can be sent here: https://massnrc.org/pests/slfreport.aspx .
The Massachusetts Department of Agricultural Resources has recently released spotted lanternfly Best Management Practices for Nurseries and Landscapers: https://massnrc.org/pests/linkeddocuments/MANurseryBMPs.pdf
And Best Management Practices for Moving Companies and the Moving Industry: https://massnrc.org/pests/linkeddocuments/SLFChecklistMovingIndustryMA.pdf
Now is a great time to provide copies of these BMP’s to employees, customers, family, and friends! The more eyes we have out there looking for spotted lanternfly, the better. Use the above BMP’s as a guide to help you inspect certain items coming from CT, DE, MD, NC, NJ, NY, OH, PA, WV, and VA.
UMass Extension is teaming up with UMass Amherst’s Department of Environmental Conservation, the USDA APHIS, and the Massachusetts Department of Agricultural Resources to monitor for the spotted lanternfly in Massachusetts. A team including members of UMass Extension’s Landscape, Nursery, and Urban Forestry Program, Extension’s Fruit Program, Stockbridge School of Agriculture, and the Department of Environmental Conservation at UMass, Amherst are undertaking a nine-month integrated research and extension project to develop effective tools to detect the spotted lanternfly.
The researchers associated with this project (Dr. Joseph Elkinton, Dr. Jeremy Andersen and Dr. Jaime Pinero) will be working with Dr. Miriam Cooperband of the USDA APHIS lab on Cape Cod to identify and evaluate airborne attractants that can improve the ability to detect SLF in traps. Dr. Cooperband has identified several attractant lures released from host plants of SLF. She is currently working on pheromones produced by SLF that may be much more attractive. The UMass team will help her conduct field tests of these new lures, while also assisting the Massachusetts Department of Agricultural Resources (MDAR) in monitoring for SLF in Massachusetts. UMass Extension Entomologist, Tawny Simisky, will periodically report on progress made during the course of this project. For more information, please visit: https://ag.umass.edu/cafe/news/looking-for-spotted-lanternfly-recent-invasive-arrival
This insect is a member of the Order Hemiptera (true bugs, cicadas, hoppers, aphids, and others) and the Family Fulgoridae, also known as planthoppers. The spotted lanternfly is a non-native species first detected in the United States in Berks County, Pennsylvania and confirmed on September 22, 2014.
For a map of known, established populations of SLF as well as detections outside of these areas where individual finds of spotted lanternfly have occurred (but no infestations are present), visit: https://nysipm.cornell.edu/environment/invasive-species-exotic-pests/spotted-lanternfly/
The spotted lanternfly is considered native to China, India, and Vietnam. It has been introduced as a non-native insect to South Korea and Japan, prior to its detection in the United States. In South Korea, it is considered invasive and a pest of grapes and peaches. The spotted lanternfly has been reported feeding on over 103 species of plants, according to new research (Barringer and Ciafré, 2020) and when including not only plants on which the insect feeds, but those that it will lay egg masses on, this number rises to 172. This includes, but is not limited to, the following: tree of heaven (Ailanthus altissima) (preferred host), apple (Malus spp.), plum, cherry, peach, apricot (Prunus spp.), grape (Vitis spp.), pine (Pinus spp.), pignut hickory (Carya glabra), sassafras (Sassafras albidum), serviceberry (Amelanchier spp.), slippery elm (Ulmus rubra), tulip poplar (Liriodendron tulipifera), white ash (Fraxinus americana), willow (Salix spp.), American beech (Fagus grandifolia), American linden (Tilia americana), American sycamore (Platanus occidentalis), big-toothed aspen (Populus grandidentata), black birch (Betula lenta), black cherry (Prunus serotina), black gum (Nyssa sylvatica), black walnut (Juglans nigra), dogwood (Cornus spp.), Japanese snowbell (Styrax japonicus), maple (Acer spp.), oak (Quercus spp.), and paper birch (Betula papyrifera).
The adults and immatures of this species damage host plants by feeding on sap from stems, leaves, and the trunks of trees. In the springtime in Pennsylvania (late April - mid-May) nymphs (immatures) are found on smaller plants and vines and new growth of trees and shrubs. Third and fourth instar nymphs migrate to the tree of heaven and are observed feeding on trunks and branches. Trees may be found with sap weeping from the wounds caused by the insect’s feeding. The sugary secretions (excrement) created by this insect may coat the host plant, later leading to the growth of sooty mold. Insects such as wasps, hornets, bees, and ants may also be attracted to the sugary waste created by the lanternflies, or sap weeping from open wounds in the host plant. Host plants have been described as giving off a fermented odor when this insect is present.
Adults are present by the middle of July in Pennsylvania and begin laying eggs by late September and continue laying eggs through late November and even early December in that state. Adults may be found on the trunks of trees such as the tree of heaven or other host plants growing in close proximity to them. Egg masses of this insect are gray in color and look similar in some ways to gypsy moth egg masses.
Host plants, bricks, stone, lawn furniture, recreational vehicles, and other smooth surfaces can be inspected for egg masses. Egg masses laid on outdoor residential items such as those listed above may pose the greatest threat for spreading this insect via human aided movement.
For more information about the spotted lanternfly, visit this fact sheet: https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/fact-sheets/spotted-lanternfly .
- Emerald Ash Borer: (Agrilus planipennis, EAB) Since the New Year, the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation has confirmed at least 22 new community detections of emerald ash borer in Massachusetts. To date, 11 out of the 14 counties in Massachusetts have confirmed emerald ash borer. (The remaining counties where EAB has yet to be detected are Barnstable, Dukes, and Nantucket counties.)A map of these locations and others previously known across the state may be found here: https://ag.umass.edu/fact-sheets/emerald-ash-borer .
This wood-boring beetle readily attacks ash (Fraxinus spp.) including white, green, and black ash and has also been found developing in white fringe tree (Chionanthus virginicus) and has been reported in cultivated olive (Olea europaea). Adult insects of this species will not be present at this time of year. Signs of an EAB infested tree may include (at this time) D-shaped exit holes in the bark (from adult emergence in previous years), “blonding” or lighter coloration of the ash bark from woodpecker feeding (chipping away of the bark as they search for larvae beneath), and serpentine galleries visible through splits in the bark, from larval feeding beneath. It is interesting to note that woodpeckers are capable of eating 30-95% of the emerald ash borer larvae found in a single tree (Murphy et al. 2018). Unfortunately, despite high predation rates, EAB populations continue to grow.
For further information about this insect, please visit: https://ag.umass.edu/fact-sheets/emerald-ash-borer . If you believe you have located EAB-infested ash trees, particularly in an area of Massachusetts not identified on the map provided, please report here: https://massnrc.org/pests/eabreport.htm .





 Gypsy Moth:(Lymantria dispar) thanks to the gypsy moth caterpillar killing fungus, Entomophaga maimaiga, the recent widespread outbreak of gypsy moth in Massachusetts has come to an end! Most locations in Massachusetts will not see damaging or even noticeable populations of this insect in 2021. However, there have been recent reports of gypsy moth caterpillars feeding on susceptible hosts in some locations in western Massachusetts, particularly in Berkshire County (ex. Alford, Great Barrington, Richmond, South Egremont, and Williamstown). (Ex. On 6/9/21, a report from Great Barrington, MA noted that caterpillars were defoliating trees in a forested area, and that caterpillar frass (excrement) was seen raining down from the canopy.) While this may be the case in certain locations, we do not expect widespread defoliation (to the extent that we saw in 2017) from this insect in 2021 in MA. Another note for 6/9/2021: there have been reports of increased gypsy moth activity in certain locations in New York. Massachusetts residents vacationing or with second homes in that state are reporting defoliation on oaks and pines in NY. For more information, visit: https://www.dec.ny.gov/animals/83118.html .
Gypsy Moth:(Lymantria dispar) thanks to the gypsy moth caterpillar killing fungus, Entomophaga maimaiga, the recent widespread outbreak of gypsy moth in Massachusetts has come to an end! Most locations in Massachusetts will not see damaging or even noticeable populations of this insect in 2021. However, there have been recent reports of gypsy moth caterpillars feeding on susceptible hosts in some locations in western Massachusetts, particularly in Berkshire County (ex. Alford, Great Barrington, Richmond, South Egremont, and Williamstown). (Ex. On 6/9/21, a report from Great Barrington, MA noted that caterpillars were defoliating trees in a forested area, and that caterpillar frass (excrement) was seen raining down from the canopy.) While this may be the case in certain locations, we do not expect widespread defoliation (to the extent that we saw in 2017) from this insect in 2021 in MA. Another note for 6/9/2021: there have been reports of increased gypsy moth activity in certain locations in New York. Massachusetts residents vacationing or with second homes in that state are reporting defoliation on oaks and pines in NY. For more information, visit: https://www.dec.ny.gov/animals/83118.html .
Gypsy moth has been in Massachusetts since the 1860's. This invasive insect from Europe often goes unnoticed, thanks to population regulation provided by the entomopathogenic fungus, E. maimaiga, as well as a NPV virus specific to gypsy moth caterpillars. (And to a lesser extent many other organisms, including other insects, small mammals, and birds who feed on gypsy moth.) However, if environmental conditions do not favor the life cycle of the fungus, outbreaks of gypsy moth caterpillars are possible. (Such as most recently from 2015-2018, with a peak in the gypsy moth population in 2017 in Massachusetts.)
Check out Episode 1 of InsectXaminer to reminisce about the 2015-2018 outbreak of this insect: https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/education-events/insectxaminer
- Asian Longhorned Beetle: (Anoplophora glabripennis, ALB) Look for signs of an ALB infestation which include perfectly round exit holes (about the size of a dime), shallow oval or round scars in the bark where a female has chewed an egg site, or sawdust-like frass (excrement) on the ground nearby host trees or caught in between branches. Be advised that other, native insects may create perfectly round exit holes or sawdust-like frass, which can be confused with signs of ALB activity.
The regulated area for Asian longhorned beetle is 110 miles2 encompassing Worcester, Shrewsbury, Boylston, West Boylston, and parts of Holden and Auburn. If you believe you have seen damage caused by this insect, such as exit holes or egg sites, on susceptible host trees like maple, please call the Asian Longhorned Beetle Eradication Program office in Worcester, MA at 508-852-8090 or toll free at 1-866-702-9938.
To report an Asian longhorned beetle find online or compare it to common insect look-alikes, visit: http://massnrc.org/pests/albreport.aspx or https://www.aphis.usda.gov/pests-diseases/alb/report .

 White Spotted Pine Sawyer (WSPS): Monochamus scutellatus adults emerge in late May throughout July, depending on local temperatures. This is a native insect in Massachusetts and is usually not a pest. Larvae develop in weakened or recently dead conifers, particularly eastern white pine (Pinus strobus). However, the white spotted pine sawyer looks very similar to the invasive Asian Longhorned Beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis, ALB. ALB adults do not emerge in Massachusetts until July and August. Beginning in July, look for the key difference between WSPS and ALB adults, which is a white spot in the top center of the wing covers (the scutellum) on the back of the beetle. White spotted pine sawyer will have this white spot, whereas Asian longhorned beetle will not. Both insects can have other white spots on the rest of their wing covers; however, the difference in the color of the scutellum is a key characteristic. See the Asian longhorned beetle entry above for more information about that non-native insect.
White Spotted Pine Sawyer (WSPS): Monochamus scutellatus adults emerge in late May throughout July, depending on local temperatures. This is a native insect in Massachusetts and is usually not a pest. Larvae develop in weakened or recently dead conifers, particularly eastern white pine (Pinus strobus). However, the white spotted pine sawyer looks very similar to the invasive Asian Longhorned Beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis, ALB. ALB adults do not emerge in Massachusetts until July and August. Beginning in July, look for the key difference between WSPS and ALB adults, which is a white spot in the top center of the wing covers (the scutellum) on the back of the beetle. White spotted pine sawyer will have this white spot, whereas Asian longhorned beetle will not. Both insects can have other white spots on the rest of their wing covers; however, the difference in the color of the scutellum is a key characteristic. See the Asian longhorned beetle entry above for more information about that non-native insect.
- Jumping Worms: In recent years, public concern about Amynthas spp. earthworms, collectively referred to as “jumping or crazy or snake” worms, has dramatically increased. University researchers and Extension groups in many locations in the US are finding that these species cause not only forest ecosystem disturbances, but may also negatively impact soil structure and reduce plant growth in gardens and managed landscapes. They do this by voraciously devouring the organic layer of the soil while feeding very close to the soil surface, unlike other species of earthworms. In woodland areas, they can quickly eat all of the leaf litter on the forest floor. Jumping worms also leave a distinct grainy soil full of worm castings. The soil becomes granular and may look like dried coffee grounds.
Unfortunately, there are currently no research-based management options available for these earthworms. So prevention is essential – preventing their introduction and spread into new areas is the best defense against them. Adult jumping worms can be 1.5 – 8 inches or more in length. Their clitellum (collar-like ring) is roughly located 1/3 down the length of the worm (from the head) and is smooth and cloudy-white and constricted. These worms may also wiggle or jump when disturbed, and can move across the ground in an S-shape like a snake. While the exact timing of their life cycle in MA might not be completely understood, their life cycle may be expected to go (roughly) something like this: they hatch in the late spring in 1-4 inches of soil, mature into adults during the summer and adults lay eggs sometime in August, and it is thought that their cocoons overwinter. (Adults perish with frost.) It is also worth noting here that jumping worms do not directly harm humans or pets.
For more information, listen to Dr. Olga Kostromytska’s presentation here: https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/education-events/invasive-insect-webinars .
Suggested reading includes Dr. Kostromytska’s recent “Hot Topics” article in Hort Notes (including an identification guide), here: https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/newsletters/hort-notes/hort-notes-2021-vol-323 .
Additional resources can also be found here:
University of Minnesota Extension: https://extension.umn.edu/identify-invasive-species/jumping-worms .
Cornell Cooperative Extension: http://ulster.cce.cornell.edu/environment/invasive-pests/jumping-worm .
UNH Extension: https://extension.unh.edu/blog/invasive-spotlight-jumping-worms .
Tree & Shrub Insects & Mites:
- Arborvitae Leafminer: In New England and eastern Canada, four species of leafminers are known to infest arborvitae. These include Argyresthia thuiella, A. freyella, A. aureoargentella, and Coleotechnites thujaella. The arborvitae leafminer, A. thuiella, is the most abundant of these and has the greatest known range when compared to the others. (It is also found in the Mid-Atlantic States and as far west as Missouri). Moths of this species appear from mid-June to mid-July and lay their eggs. The damage caused by all of these species is nearly identical. Trees, however, have been reported to lose up to 80% of their foliage due to arborvitae leafminer and still survive. At least 27 species of parasites have been reported as natural enemies of arborvitae leafminers, the most significant of which may be a parasitic wasp (Pentacnemus bucculatricis). Arborvitae leafminer damage causes the tips of shoots and foliage to turn yellow and brown. If infestations are light, prune out infested tips.

 Azalea Sawflies: There are a few species of sawflies that impact azaleas. Johnson and Lyon's Insects that Feed on Trees and Shrubs mentions three of them. Amauronematus azaleae was first reported in New Hampshire in 1895 and is likely found in most of New England. Adults of this species are black with some white markings and wasp-like. Generally green larvae feed mostly on mollis hybrid azaleas. Remember, sawfly caterpillars have at least enough abdominal prolegs to spell “sawfly” (so 6 or more prolegs). Adults are present in May, and females lay their eggs and then larvae hatch and feed through the end of June. There is one generation per year. Nematus lipovskyi has been reared from swamp azalea (Rhododendron viscosum). Adults of that species have been collected in April (in states to the south) and May (in New England) and larval feeding is predominantly in late April and May in Virginia and June in New England. One generation of this species occurs per year, and most mollis hybrid azaleas can be impacted. A third species, Arge clavicornis, is found as an adult in July and lays its eggs in leaf edges in rows. Larvae are present in August and September. Remember, Bacillus thuringiensis Kurstaki does not manage sawflies.
Azalea Sawflies: There are a few species of sawflies that impact azaleas. Johnson and Lyon's Insects that Feed on Trees and Shrubs mentions three of them. Amauronematus azaleae was first reported in New Hampshire in 1895 and is likely found in most of New England. Adults of this species are black with some white markings and wasp-like. Generally green larvae feed mostly on mollis hybrid azaleas. Remember, sawfly caterpillars have at least enough abdominal prolegs to spell “sawfly” (so 6 or more prolegs). Adults are present in May, and females lay their eggs and then larvae hatch and feed through the end of June. There is one generation per year. Nematus lipovskyi has been reared from swamp azalea (Rhododendron viscosum). Adults of that species have been collected in April (in states to the south) and May (in New England) and larval feeding is predominantly in late April and May in Virginia and June in New England. One generation of this species occurs per year, and most mollis hybrid azaleas can be impacted. A third species, Arge clavicornis, is found as an adult in July and lays its eggs in leaf edges in rows. Larvae are present in August and September. Remember, Bacillus thuringiensis Kurstaki does not manage sawflies.
 Bagworm: Thyridopteryx ephemeraeformis is a native species of moth whose larvae construct bag-like coverings over themselves with host plant leaves and twigs. This insect overwinters in the egg stage, within the bags of deceased females from last season. Eggs have hatched and very small, young larvae are observed feeding, as is typical around mid-June, or roughly between 600-900 GDD’s. In certain areas across MA in 2020, increased populations of bagworms were observed and reported, particularly in urban forest settings and managed landscapes. More information can be found here: https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/fact-sheets/bagworm .
Bagworm: Thyridopteryx ephemeraeformis is a native species of moth whose larvae construct bag-like coverings over themselves with host plant leaves and twigs. This insect overwinters in the egg stage, within the bags of deceased females from last season. Eggs have hatched and very small, young larvae are observed feeding, as is typical around mid-June, or roughly between 600-900 GDD’s. In certain areas across MA in 2020, increased populations of bagworms were observed and reported, particularly in urban forest settings and managed landscapes. More information can be found here: https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/fact-sheets/bagworm .- Cottony Taxus Scale: Pulvinaria floccifera, also referred to as the cottony camellia scale, utilizes such hosts as taxus, camellia, holly, hydrangea, Japanese maple, euonymus, magnolia, and jasmine, among others. Females have laid the long, narrow, white and fluffy egg sac that makes them much more noticeable. Eggs will hatch over an extended period of 6 weeks and crawlers may be treated between 802-1388 GDD’s. This insect can cause the host to appear off-color. They also produce honeydew which promotes sooty mold growth. Dieback is not common with this insect. Target the underside of the foliage. Horticultural oil, neem oil, and insecticidal soaps may be used to manage these soft scales. Reduced risk options help preserve natural enemies.
- Dogwood Borer: Synanthedon scitula is a species of clearwing moth whose larvae bore not only into dogwood (Cornus), but hosts also include flowering cherry, chestnut, apple, mountain ash, hickory, pecan, willow, birch, bayberry, oak, hazel, myrtle, and others. Kousa dogwood appear to be resistant to this species. Signs include the sloughing of loose bark, brown frass, particularly near bark cracks and wounds, dead branches, and adventitious growth. The timing of adult emergence can be expected when dogwood flower petals are dropping and weigela begins to bloom. Adult moth flights continue from then until September. Emergence in some hosts (ex. apple) appears to be delayed, but this differs depending upon the location in this insect’s range. Eggs are laid singly, or in small groups, on smooth and rough bark. Female moths preferentially lay eggs near wounded bark. After hatch, larvae wander until they find a suitable entrance point into the bark. This includes wounds, scars, or branch crotches. This insect may also be found in twig galls caused by other insects or fungi. Larvae feed on phloem and cambium. Fully grown larvae are white with a light brown head and approx. ½ inch long. Pheromone traps and lures are useful for determining the timing of adult moth emergence and subsequent management.

 Dogwood Sawfly: Macremphytus tarsatus larvae are commonly seen feeding on dogwoods, especially gray dogwood (Cornus racemosa). One generation occurs per year. The larvae of the dogwood sawfly overwinter in decaying wood and occasionally (rarely) compromised structural timber. An overwintering “cell” is created in this soft wood. Pupation occurs in the springtime and adults can take a lengthy time to emerge, roughly from late May through July. 100+ eggs are laid in groups on the underside of leaves. Eggs hatch and the larvae feed gregariously, initially skeletonizing the leaves. As the caterpillars grow in size, they are capable of eating the entire leaf, leaving only midveins behind. Larval appearance varies greatly throughout instars. Early instars are translucent and yellow, but as the caterpillars grow, they develop black spots (over the yellow) and become covered in a white powder-like material. Larvae and their shed skins may resemble bird droppings. Full-grown larvae begin to wander in search of a suitable overwintering location. Rotting wood lying on the ground is preferred for this. Sawfly caterpillars can be collected from plants and dropped into a can of soapy water.
Dogwood Sawfly: Macremphytus tarsatus larvae are commonly seen feeding on dogwoods, especially gray dogwood (Cornus racemosa). One generation occurs per year. The larvae of the dogwood sawfly overwinter in decaying wood and occasionally (rarely) compromised structural timber. An overwintering “cell” is created in this soft wood. Pupation occurs in the springtime and adults can take a lengthy time to emerge, roughly from late May through July. 100+ eggs are laid in groups on the underside of leaves. Eggs hatch and the larvae feed gregariously, initially skeletonizing the leaves. As the caterpillars grow in size, they are capable of eating the entire leaf, leaving only midveins behind. Larval appearance varies greatly throughout instars. Early instars are translucent and yellow, but as the caterpillars grow, they develop black spots (over the yellow) and become covered in a white powder-like material. Larvae and their shed skins may resemble bird droppings. Full-grown larvae begin to wander in search of a suitable overwintering location. Rotting wood lying on the ground is preferred for this. Sawfly caterpillars can be collected from plants and dropped into a can of soapy water.

 Elm Casebearer: Coleophora ulmifoliella is a native North American moth that is found throughout New England and west to Michigan. Host plants include American, red, and slippery elm. Moths are tiny, with wing spans of approximately 13 mm. and buff in color with gray markings. According to Johnson and Lyon’s “Insects that Feed on Trees and Shrubs”, adult moths fly and mate and females lay eggs in July, at which point the eggs hatch and the larvae of the insect enter the host plant leaves to feed as miners between the epidermal layers of the leaf. As the larva grows in size, it emerges from the leaf it was mining and creates a case, which grows in size with it. This case serves as a protective covering, which the larva adorns itself with through the rest of the larval stage. Mines look like rectangular spots in the leaves that are brown in color. As the weather cools in the fall, the casebearer larva migrates to the twigs of its host plant, where it ties the case in one location to spend the winter as an immature larva. The following spring, the casebearer migrates to new leaves and resumes feeding as a miner, however it does this while dragging its case behind it and never allowing its body to completely leave the case. Elm casebearer cases are approximately 6 mm. in length. Once fully mature, the larvae pupate (within their individual cases) and adult moths emerge in July. A single generation occurs per year.
Elm Casebearer: Coleophora ulmifoliella is a native North American moth that is found throughout New England and west to Michigan. Host plants include American, red, and slippery elm. Moths are tiny, with wing spans of approximately 13 mm. and buff in color with gray markings. According to Johnson and Lyon’s “Insects that Feed on Trees and Shrubs”, adult moths fly and mate and females lay eggs in July, at which point the eggs hatch and the larvae of the insect enter the host plant leaves to feed as miners between the epidermal layers of the leaf. As the larva grows in size, it emerges from the leaf it was mining and creates a case, which grows in size with it. This case serves as a protective covering, which the larva adorns itself with through the rest of the larval stage. Mines look like rectangular spots in the leaves that are brown in color. As the weather cools in the fall, the casebearer larva migrates to the twigs of its host plant, where it ties the case in one location to spend the winter as an immature larva. The following spring, the casebearer migrates to new leaves and resumes feeding as a miner, however it does this while dragging its case behind it and never allowing its body to completely leave the case. Elm casebearer cases are approximately 6 mm. in length. Once fully mature, the larvae pupate (within their individual cases) and adult moths emerge in July. A single generation occurs per year.
Damage from a single elm casebearer larva is negligible and does not require management. However, on occasion, elevated populations of this insect do occur and noticeable injury to host plant leaves can transpire. Complete browning and death of leaves can occur, if high populations are present. Chemical management of this native insect is not necessary unless the majority of leaves contain more than a single larva.
- Elongate Hemlock Scale: Fiorinia externa is found on eastern, Carolina, and Japanese hemlock, as well as yew, spruce, and fir. The elongate hemlock scale may overwinter in various life stages, and overlap of many developmental stages at any given time can be observed throughout much of the season. Treatments for the crawler, or mobile, stage of this insect may be made in late May through mid-June, or between 360-700 GDD’s, base 50°F. Nitrogen fertilizer applications may make elongate hemlock scale infestations worse.
- Euonymus Scale: Unaspis euonymi is an armored scale that can be found on euonymus, holly, bittersweet, and pachysandra. This insect can cause yellow spotting on leaves, dieback, and distorted bark. For crawlers, early June timing is suggested between 533-820 GDD’s. (Eggs begin to hatch in early June.)


 European Pine Sawfly: Neodiprion sertifer overwinters in the egg stage. Eggs are laid by females the previous season by cutting slits in needles using their ovipositors and depositing 6-8 eggs in each of 10-12 needles. Egg hatch occurs from late-April to mid-May and caterpillars become active roughly between 78-220 GDD, base 50°F. The primary host in MA is Mugo pine but it can be found on Scots, red, jack, and Japanese red pine. It is also found on white, Austrian, ponderosa, shortleaf, and pitch pine when planted near the aforementioned species. This dark colored caterpillar feeds in tight groups and small numbers can be pruned or plucked out of host plants and destroyed. Spinosad products can be used whenever the caterpillars are actively feeding, usually by mid-May and when caterpillars are still small. Bacillus thuringiensis kurstaki is not effective against sawflies.
European Pine Sawfly: Neodiprion sertifer overwinters in the egg stage. Eggs are laid by females the previous season by cutting slits in needles using their ovipositors and depositing 6-8 eggs in each of 10-12 needles. Egg hatch occurs from late-April to mid-May and caterpillars become active roughly between 78-220 GDD, base 50°F. The primary host in MA is Mugo pine but it can be found on Scots, red, jack, and Japanese red pine. It is also found on white, Austrian, ponderosa, shortleaf, and pitch pine when planted near the aforementioned species. This dark colored caterpillar feeds in tight groups and small numbers can be pruned or plucked out of host plants and destroyed. Spinosad products can be used whenever the caterpillars are actively feeding, usually by mid-May and when caterpillars are still small. Bacillus thuringiensis kurstaki is not effective against sawflies.- Hemlock Looper: Two species of geometrid moths in the genus Lambdina are native insects capable of defoliating eastern hemlock, balsam fir, and white spruce. Adult moths lay their eggs on the trunk and limbs of hosts in September and October, and eggs will hatch by late May or early June. (L. fiscellaria caterpillars may be active between 448-707 GDD’s.) Monitor susceptible hosts for small, inch-worm like caterpillars. Where populations are low, no management is necessary. Hemlock loopers have several effective natural enemies.


 Hemlock Woolly Adelgid: Adelges tsugae is present on eastern and Carolina hemlock. The overwintering hemlock woolly adelgid generation (sistens) is present through mid-spring and produces the spring generation (progrediens) which will be present from early spring through mid-summer. HWA, unlike many other insects, does most of its feeding over the winter. Eggs may be found in woolly masses at the base of hemlock needles beginning in mid-March. Each woolly mass is created by a female who may then lay 50-300 eggs. Eggs hatch and crawlers may be found from mid-March through mid-July. Infested trees may be treated with foliar sprays in late April to early May, using Japanese quince as a phenological indicator. Systemic applications may be made in the spring and fall, or when soil conditions are favorable for translocation to foliage. Nitrogen fertilizer applications may make hemlock woolly adelgid infestations worse.
Hemlock Woolly Adelgid: Adelges tsugae is present on eastern and Carolina hemlock. The overwintering hemlock woolly adelgid generation (sistens) is present through mid-spring and produces the spring generation (progrediens) which will be present from early spring through mid-summer. HWA, unlike many other insects, does most of its feeding over the winter. Eggs may be found in woolly masses at the base of hemlock needles beginning in mid-March. Each woolly mass is created by a female who may then lay 50-300 eggs. Eggs hatch and crawlers may be found from mid-March through mid-July. Infested trees may be treated with foliar sprays in late April to early May, using Japanese quince as a phenological indicator. Systemic applications may be made in the spring and fall, or when soil conditions are favorable for translocation to foliage. Nitrogen fertilizer applications may make hemlock woolly adelgid infestations worse.
 Imported Willow Leaf Beetle: Plagiodera versicolora adult beetles overwinter near susceptible hosts. Adult beetles will chew holes and notches in the leaves of willow once they become available. Females lay yellow eggs in clusters on the undersides of leaves. Larvae are slug-like and bluish-green in color. They will feed in clusters and skeletonize the leaves. Most plants can tolerate the feeding from this insect, and foliage will appear brown. Repeated yearly feeding can be an issue, in which case management of the young larvae may be necessary. Take care with treatment in areas near water.
Imported Willow Leaf Beetle: Plagiodera versicolora adult beetles overwinter near susceptible hosts. Adult beetles will chew holes and notches in the leaves of willow once they become available. Females lay yellow eggs in clusters on the undersides of leaves. Larvae are slug-like and bluish-green in color. They will feed in clusters and skeletonize the leaves. Most plants can tolerate the feeding from this insect, and foliage will appear brown. Repeated yearly feeding can be an issue, in which case management of the young larvae may be necessary. Take care with treatment in areas near water.
Check out Episode 4 of InsectXaminer to see the imported willow leaf beetle in action and learn more about its life cycle: https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/education-events/insectxaminer .
- Lacebugs: Stephanitis spp. lacebugs such as S. pyriodes can cause severe injury to azalea foliage. S. rhododendri can be common on rhododendron and mountain laurel. S. takeyai has been found developing on Japanese andromeda, leucothoe, styrax, and willow. Stephanitis spp. lace bug activity should be monitored through September. Before populations become too large, treat with a summer rate horticultural oil spray as needed. Be sure to target the undersides of the foliage in order to get proper coverage of the insects. Certain azalea and andromeda cultivars may be less preferred by lace bugs.
- Lilac Borer: Podosesia syringae is a clearwing moth pest of lilac, privet, fringetree, and ash. (It is also known as the ash borer, not to be confused with the emerald ash borer.) Adults mimic paper wasps. Larvae are wood-boring, and signs and symptoms include branch dieback, holes, and occasionally, sawdust-like frass accumulated on bark. Larvae bore into stems, trunks, and branches, chewing an irregularly shaped entrance hole. Peak adult moth flights may occur in the northern portion of this insect’s range in June and is usually over by August 1st. Pheromone traps can be used to time adult emergence. Adult females lay flattened, oval, and tan eggs that are deposited singly or in clusters on bark crevices, ridges, and sometimes smooth bark; but usually laid in or near wounds in the bark. On average, 395 eggs are laid by each female. After hatch, larvae chew into the bark and feed laterally and then vertically in phloem tissue. Larvae overwinter in tunnels in the final instar and resume feeding in the spring. Adults emerge through a round exit hole (4-5 mm. in diameter). This insectmay be targeted between 200-299 GDD’s, base 50°F.


 Lily Leaf Beetle: Lilioceris lilii adults overwinter in sheltered places. As soon as susceptible hosts such as Lilium spp. (Turk’s cap, tiger, Easter, Asiatic, and Oriental lilies) and Fritillaria spp. break through the ground, the adult lily leaf beetles are known to feed on the new foliage. (Note: daylilies are not hosts.) Typically, in May, mating will occur and each female will begin to lay 250-450 eggs in neat rows on the underside of the foliage. If there are only a few plants in the garden, hand picking and destroying overwintering adults can help reduce local garden-level populations at that time. As eggs hatch and growing larvae begin to feed, the larvae of this insect can be removed from plants as well.
Lily Leaf Beetle: Lilioceris lilii adults overwinter in sheltered places. As soon as susceptible hosts such as Lilium spp. (Turk’s cap, tiger, Easter, Asiatic, and Oriental lilies) and Fritillaria spp. break through the ground, the adult lily leaf beetles are known to feed on the new foliage. (Note: daylilies are not hosts.) Typically, in May, mating will occur and each female will begin to lay 250-450 eggs in neat rows on the underside of the foliage. If there are only a few plants in the garden, hand picking and destroying overwintering adults can help reduce local garden-level populations at that time. As eggs hatch and growing larvae begin to feed, the larvae of this insect can be removed from plants as well.
Check out Episode 3 of InsectXaminer to see the lily leaf beetle in action and learn more about its life cycle: https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/education-events/insectxaminer .
[editor's note: Also see the blue box at the end of this Insect Section for a chance to help with LLB tracking and/or citizen science.]

 Oak Shothole Leafminer: The oak shothole leafminer (Japanagromyza viridula synonym Agromyza viridula) is considered native to the United States, although very little is known about this species and other agromyzid leaf miners. It is reportedly found throughout the eastern U.S. from Maine to Georgia, and likely the entire eastern half of the United States. The damage caused by the activity of the adult female oak shothole leafminer is characteristic of this fly species. Adult female flies are active when red and white oak buds are just opening and until the newly developing leaves are approximately 5 cm (~2") in length. The holes seen in these images were created when the leaves were no more than 4.5 cm (~1 3/4") long. This damage is caused by the adult female fly feeding. Because the fly’s mouthparts are unable to pierce the newly developing leaf tissue, it uses its ovipositor to cause enough damage such that any fluids leaking from the leaf can then be lapped up. The female fly will move the ovipositor in side-to-side and circular motions, creating initial injury that is no more than 0.7 mm (~3/100") at its widest point on the tiny, newly developing leaves. The area injured by this action soon turns brown and dries, eventually forming a small disk. This disk of necrotic tissue often remains conspicuously attached to the expanding hole formed in the leaf. As the leaves grow in size, the damage from these flies enlarges, and the holes are described to be approximately six times the size of the original injury created by these tiny flies, who are themselves about 3 mm (~1/10") in length. Occasionally, the female fly will lay an egg in the leaf tissue.
Oak Shothole Leafminer: The oak shothole leafminer (Japanagromyza viridula synonym Agromyza viridula) is considered native to the United States, although very little is known about this species and other agromyzid leaf miners. It is reportedly found throughout the eastern U.S. from Maine to Georgia, and likely the entire eastern half of the United States. The damage caused by the activity of the adult female oak shothole leafminer is characteristic of this fly species. Adult female flies are active when red and white oak buds are just opening and until the newly developing leaves are approximately 5 cm (~2") in length. The holes seen in these images were created when the leaves were no more than 4.5 cm (~1 3/4") long. This damage is caused by the adult female fly feeding. Because the fly’s mouthparts are unable to pierce the newly developing leaf tissue, it uses its ovipositor to cause enough damage such that any fluids leaking from the leaf can then be lapped up. The female fly will move the ovipositor in side-to-side and circular motions, creating initial injury that is no more than 0.7 mm (~3/100") at its widest point on the tiny, newly developing leaves. The area injured by this action soon turns brown and dries, eventually forming a small disk. This disk of necrotic tissue often remains conspicuously attached to the expanding hole formed in the leaf. As the leaves grow in size, the damage from these flies enlarges, and the holes are described to be approximately six times the size of the original injury created by these tiny flies, who are themselves about 3 mm (~1/10") in length. Occasionally, the female fly will lay an egg in the leaf tissue.
The eggs hatch and mining from the larvae of the oak shothole leafminer is reported to occur in the second week of June in Maine, while in Ohio there are reports that the blotch mines created by this insect are most evident in early to mid-May in that state. Reportedly, fully grown larvae emerge from their mines to drop to the soil to pupate. Johnson and Lyon (1991) states that although adults are present the following spring, they may also reappear later in the same season “if a second flush of growth takes place or water sprouts (epicormic shoots) develop”. The oak shothole leafminer is not usually considered a significant pest of oak, and the damage it causes typically does not have a significant impact on the overall health of the tree. However, in a 1967 paper detailing observations from the 1960’s in Maine, there is a question about the economic importance of this species on ornamental oaks. In 1964, an “abundance of neat, prominent holes in foliage of ornamental red and white oaks (Quercus borealis var. maxima and Q. alba) in southern Maine” was observed. This was again observed in 1965. The cause, at the time determined to be Japanagromyza viridula, was identified by the State Entomologist with the Maine Forest Service and partners in the USDA. Their observations stated that many more “punctures” are made by the female for feeding than for oviposition (egg laying) and this is a common pattern of flies in this family. This might explain why the damage from the feeding adult females seems so extensive, whereas the mines from the feeding larvae of this insect are not present in the same proportion and may even be difficult to find.

 Oak Leafrolling Weevil: Synolabus bipustulatus (synonym Attelabus bipustulatus) is a small, stout, shiny, black weevil with two red spots, one on each elytra (hardened hindwing). (Another oak leaf rolling weevil species exists, Homoeolabus analis, but that insect is primarily orange in color with the exception of a black head and legs.) Weevils of this species (S. bipustulatus) are less than ¼ inch in size. The exact timing of this insect’s life cycle in Massachusetts is not completely understood, but adult weevils were observed by the Massachusetts Department of Agricultural Resources and reported to UMass Extension on 6/10/2021 from Middlesex County, Massachusetts. Adult weevils chew slits on either side of the midrib of the host plant leaf, where they will lay an egg at the tip of the leaf. The leaf is then folded (by the weevil) along the midrib and rolled into a tidy cylinder, kind of like a sleeping bag. By the end of this rolling, the egg is positioned near the center of the roll. Once the egg hatches, the immature weevil larva (which is legless, curved, and plump with a brown head) feeds on the tissue inside the rolled leaf. Once the larva matures, it pupates inside the rolled leaf. Adults emerge again to continue the life cycle and there may be multiple generations per year in certain locations of this insect’s geographic range. Leafrolling weevils have been noted on 16 species of oak and 2 species of chestnut. These insects are rarely considered pests, as they typically do not cause noticeable damage to their host plants. Management is seldom considered necessary.
Oak Leafrolling Weevil: Synolabus bipustulatus (synonym Attelabus bipustulatus) is a small, stout, shiny, black weevil with two red spots, one on each elytra (hardened hindwing). (Another oak leaf rolling weevil species exists, Homoeolabus analis, but that insect is primarily orange in color with the exception of a black head and legs.) Weevils of this species (S. bipustulatus) are less than ¼ inch in size. The exact timing of this insect’s life cycle in Massachusetts is not completely understood, but adult weevils were observed by the Massachusetts Department of Agricultural Resources and reported to UMass Extension on 6/10/2021 from Middlesex County, Massachusetts. Adult weevils chew slits on either side of the midrib of the host plant leaf, where they will lay an egg at the tip of the leaf. The leaf is then folded (by the weevil) along the midrib and rolled into a tidy cylinder, kind of like a sleeping bag. By the end of this rolling, the egg is positioned near the center of the roll. Once the egg hatches, the immature weevil larva (which is legless, curved, and plump with a brown head) feeds on the tissue inside the rolled leaf. Once the larva matures, it pupates inside the rolled leaf. Adults emerge again to continue the life cycle and there may be multiple generations per year in certain locations of this insect’s geographic range. Leafrolling weevils have been noted on 16 species of oak and 2 species of chestnut. These insects are rarely considered pests, as they typically do not cause noticeable damage to their host plants. Management is seldom considered necessary.
- Spruce Spider Mite: Oligonychus ununguis is a cool-season mite that becomes active in the spring from tiny eggs that have overwintered on host plants. Hosts include spruce, arborvitae, juniper, hemlock, pine, Douglas-fir, and occasionally other conifers. This particular species becomes active in the spring and can feed, develop, and reproduce through roughly June. When hot, dry summer conditions begin, this spider mite will enter a summer-time dormant period (aestivation) until cooler temperatures return in the fall. This particular mite may prefer older needles to newer ones for food. Magnification is required to view spruce spider mite eggs. Tapping host plant branches over white paper may be a useful tool when scouting for spider mite presence. (View with a hand lens.) Spider mite damage may appear on host plant needles as yellow stippling and occasionally fine silk webbing is visible.
Spruce spider mite populations may again build (with subsequent generations) in mid-late May (192-363 GDD’s) and again in late August to mid-September (2375-2806 GDD’s). Continue to scout for spruce spider mite by tapping branches over a white piece of paper or other white surface, then viewing them with a hand lens or other magnification. A general rule of thumb is that if 10 or more spruce spider mites are found per branch (in the absence of predatory mites), chemical management might be necessary (if you are also seeing roughly 10% of the foliage with stippling/discoloration). However, if you are finding light-colored and tear-drop shaped and fast-moving predatory mites, at a ratio of approximately 1 predatory mite: 10 spruce spider mites, these beneficial insect relatives may be able to help naturally keep spruce spider mite populations below damaging levels. It is important to also scout for predatory mites and beneficial insects (hover fly larvae, lacewing larvae, and lady beetle larvae and adults) while scouting for spruce spider mite, because knowledge of the presence of these beneficial predators will impact your management decisions. Broad spectrum insecticides/miticides should not be used to manage spruce spider mite on host plants where predatory mites are present as these chemicals could kill the predatory mites and lead to a subsequent surge in spruce spider mite populations.
 Taxus Mealybug: Dysmicoccus wistariae will produce honeydew and lead to sooty mold growth, yellowing of needles, and sparsely foliated plants. Eventual dieback may be possible. This species is commonly associated with taxus in New England, but can be occasionally found on dogwood, rhododendron, Prunus spp., maple, andromeda, and crabapple. These mealybugs are found on stems and branches and particularly like to congregate at branch crotches. Taxus mealybug feeds in the inner bark tissue of the trunk and branches. Adult females are present from June to August and give birth to living young in the summer. Immatures overwinter. A single generation may occur per year in New England, but areas to the south can have multiple generations of this insect. Management may be targeted between 246-618 GDD’s, base 50°F. Horticultural oil and neem oil may be used.
Taxus Mealybug: Dysmicoccus wistariae will produce honeydew and lead to sooty mold growth, yellowing of needles, and sparsely foliated plants. Eventual dieback may be possible. This species is commonly associated with taxus in New England, but can be occasionally found on dogwood, rhododendron, Prunus spp., maple, andromeda, and crabapple. These mealybugs are found on stems and branches and particularly like to congregate at branch crotches. Taxus mealybug feeds in the inner bark tissue of the trunk and branches. Adult females are present from June to August and give birth to living young in the summer. Immatures overwinter. A single generation may occur per year in New England, but areas to the south can have multiple generations of this insect. Management may be targeted between 246-618 GDD’s, base 50°F. Horticultural oil and neem oil may be used.
- Twolined Chestnut Borer: Agrilus bilineatus is a native jewel beetle (also known as a flatheaded borer) in the Family Buprestidae. This insect is also in the same genus as the invasive emerald ash borer. The twolined chestnut borer is native to Massachusetts, much of New England, and the eastern United States. This species has one generation per year and adults are typically active from April – August, depending upon location and temperature. Adults will conduct some maturation feeding on oak prior to mating. Females will lay clusters of tiny eggs in the cracks and crevices of bark. Larvae hatch from the eggs in 1-2 weeks and burrow through the bark into the cambium, where they feed in a similar manner to the emerald ash borer, creating meandering galleries as they feed. (The galleries of the twolined chestnut borer can be straight in very stressed trees.) Larvae typically mature by August – October and burrow to the outer bark where they create a chamber in which they overwinter. Pupation occurs the following spring and adults emerge through D-shaped exit holes that are approximately 1/5 inch wide. In the northern extent of this insect’s range, they can take 2 years to complete their life cycle. Larvae of this insect have been recorded from eastern white oak, common post oak, burr oak, scarlet oak, northern red oak, and eastern black oak. Adults have been recorded on fir and pin oak. These insects are attracted to stressed host plants and typically become a secondary factor in the decline of the tree.
- Two-Spotted Spider Mite: Tetranychus urticae is a “warm-season” mite that loves hot and dry weather, which may favor the quick reproduction and build-up of this pest. Management should seek to preserve beneficial predatory mites. Monitor susceptible hosts (elm, maple, redbud, ash, black locust, tuliptree, and many deciduous shrubs) for increasing numbers of these mites until mid-August. Mites will be found on the undersides of leaves and cause stippling of the foliage.
- Viburnum Leaf Beetle: Pyrrhalta viburni is a beetle in the family Chrysomelidae that is native to Europe, but was found in Massachusetts in 2004. Viburnum leaf beetle overwinters as eggs laid in capped pits on the newest growth of susceptible viburnum branches. Scout for overwintered eggs and prune out and destroy before they hatch. Egg hatch occurs in late-April to early-May as temperatures warm and foliage becomes available. Monitor for larvae in mid-May (80-120 GDD’s). This beetle feeds exclusively on many different species of viburnum, which includes, but is not limited to, susceptible plants such as V. dentatum, V. nudum, V. opulus, V. propinquum, and V. rafinesquianum. Some viburnum have been observed to have varying levels of resistance to this insect, including but not limited to V. bodnantense, V. carlesii, V. davidii, V. plicatum, V. rhytidophyllum, V. setigerum, and V. sieboldii. More information about viburnum leaf beetle may be found at http://www.hort.cornell.edu/vlb/ .
 Woolly Apple Aphid: Eriosoma lanigerum may be found on apple, crabapple, hawthorn, mountain-ash, Pyracantha, and elm hosts. The primary (winter) host is elm, on which aphids infest emerging spring leaves, causing leaves to curl or close into stunted, rosette-like clusters found at twig tips. Woolly apple aphid was observed on elm on 6/1/2021 in Amherst, MA. Rosettes at this location are full of honeydew producing aphids. On apple and crabapple, this species of aphid colonizes roots, trunks, and branches in the summer and is commonly found near previous wounds or callous tissue. On roots, the aphids cause swelled areas which can girdle and kill roots. The aphids, when found in above ground plant parts such as elm leaves, are covered with white wax. Eggs are the overwintering stage on elm, which hatch in the spring in time for the nymphs to infest new elm foliage. Following a few generations on elm, the aphids will develop into a winged form, which will disperse and seek out apple and crabapple. Multiple generations will occur on these alternate hosts in the summer and by the fall, a winged form will return to elm and mated females will lay eggs near elm buds. These aphids are a favorite snack for insect predators such as the multicolored Asian lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis.
Woolly Apple Aphid: Eriosoma lanigerum may be found on apple, crabapple, hawthorn, mountain-ash, Pyracantha, and elm hosts. The primary (winter) host is elm, on which aphids infest emerging spring leaves, causing leaves to curl or close into stunted, rosette-like clusters found at twig tips. Woolly apple aphid was observed on elm on 6/1/2021 in Amherst, MA. Rosettes at this location are full of honeydew producing aphids. On apple and crabapple, this species of aphid colonizes roots, trunks, and branches in the summer and is commonly found near previous wounds or callous tissue. On roots, the aphids cause swelled areas which can girdle and kill roots. The aphids, when found in above ground plant parts such as elm leaves, are covered with white wax. Eggs are the overwintering stage on elm, which hatch in the spring in time for the nymphs to infest new elm foliage. Following a few generations on elm, the aphids will develop into a winged form, which will disperse and seek out apple and crabapple. Multiple generations will occur on these alternate hosts in the summer and by the fall, a winged form will return to elm and mated females will lay eggs near elm buds. These aphids are a favorite snack for insect predators such as the multicolored Asian lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis.
 Woolly Beech (Leaf) Aphid: Phyllaphis fagi is a species of aphid commonly found on the leaf undersides of European beech, Fagus sylvatica, and its cultivars. This is a European species that is now widely distributed throughout North America. All life stages of this particular aphid occur on European beech foliage. European beech trees in North America have been observed as capable of holding large populations of this aphid year after year with little to no visible injury to the tree. Like their other aphid brethren, the woolly beech leaf aphid can create large quantities of sticky honeydew. These aphids were observed on Fagus sylvatica 'Asplenifolia' in Amherst, MA on 6/1/2021. The woolly beech leaf aphid is sometimes confused with another woolly aphid, also known as the beech blight aphid (Grylloprociphilus imbricator), which is only found on American beech, Fagus grandifolia. G. imbricator has an alternate common name, the boogie-woogie aphid, due to a behavior where this species, when colonies are disturbed, can wiggle (or dance) together, perhaps in an effort to distract potential predators.
Woolly Beech (Leaf) Aphid: Phyllaphis fagi is a species of aphid commonly found on the leaf undersides of European beech, Fagus sylvatica, and its cultivars. This is a European species that is now widely distributed throughout North America. All life stages of this particular aphid occur on European beech foliage. European beech trees in North America have been observed as capable of holding large populations of this aphid year after year with little to no visible injury to the tree. Like their other aphid brethren, the woolly beech leaf aphid can create large quantities of sticky honeydew. These aphids were observed on Fagus sylvatica 'Asplenifolia' in Amherst, MA on 6/1/2021. The woolly beech leaf aphid is sometimes confused with another woolly aphid, also known as the beech blight aphid (Grylloprociphilus imbricator), which is only found on American beech, Fagus grandifolia. G. imbricator has an alternate common name, the boogie-woogie aphid, due to a behavior where this species, when colonies are disturbed, can wiggle (or dance) together, perhaps in an effort to distract potential predators.
- Woolly Elm Aphid: Eriosoma americanum females lay a single egg in the cracks and crevices of elm bark, where the egg overwinters. Eggs hatch on elm in the spring as leaves are unfolding. Aphids may be active from 121-246 GDD’s, base 50°F on elm. A young, wingless female hatched from the egg feeds on the underside of leaf tissue. This female aphid matures and gives birth to 200 young, all females, without mating. These aphids feed, and the elm leaf curls around them and protects them. By the end of June, winged migrants mature and find serviceberry hosts. Another set of females is produced. These new females crawl to and begin feeding on the roots of serviceberry. Multiple generations occur on the roots of serviceberry through the summer.
Concerned that you may have found an invasive insect or suspicious damage caused by one? Need to report a pest sighting? If so, please visit the Massachusetts Introduced Pests Outreach Project: http://massnrc.org/pests/pestreports.htm .
Reported by Tawny Simisky, Extension Entomologist, UMass Extension Landscape, Nursery, & Urban Forestry Program
A Message from the University of Rhode Island Biocontrol Lab and Carleton University:
 Hello fellow gardeners, naturalists, and lily enthusiasts,
Hello fellow gardeners, naturalists, and lily enthusiasts,
It has been twenty years since biological control agents (parasitic wasps) were first released in North America to combat the lily leaf beetle, a destructive pest of Asiatic lilies and fritillaries in gardens as well as native lilies in natural areas. In many areas, control of the beetle has been so effective that it is now hard to find lily beetles. However, there are still some areas where the beetle is spreading unchecked.
At this time, it is important for us to update the status of the lily leaf beetle and its biocontrol agents across North America. This will help us determine how effective the agents are and how far they have spread from the release sites. We will also be able to prioritize areas that are heavily hit by the beetle for the next releases.
Please help us with this task by visiting the lily beetle tracker website and responding to a very short survey. There is also an opportunity, explained on the website, to help us gather data on parasitism rates across the country—this would make a good project for homeschooled kids.
https://lilybeetletracker.weebly.com/new-2021-citizen-science.html
Please share the link with your gardening groups, naturalists' groups and anyone else who might be interested.
Many thanks and have a lovely summer,
Naomi Cappuccino, Carleton University
Lisa Tewksbury and Dick Casagrande, University of Rhode Island Biocontrol Lab
For More Information, Visit:
https://web.uri.edu/biocontrol/lily-leaf-beetle-larval-collections-2016/llb-citizen-science-2020/#
Weeds
New growth expansion of poison ivy continues. Poison ivy is flowering so it should be treated now. Glyphosate or triclopyr are the best herbicides for poison ivy control and applications can be done from now until mid-September. Triclopyr products should be selected over glyphosate products in areas were grasses need to be saved. Contact (Scythe, Reward) or the non-chemical/organic herbicide products will provide “burndown” activity only and will not adequately control poison ivy.
Many people are asking if glufosinate (Finale or Cheetah Pro) can be used as a replacement for glyphosate. Glufosinate and glyphosate are both non-selective, postemergence herbicides. Glufosinate is not translocated or only limitedly so, whereas glyphosate is strongly translocated. Translocation is the movement of an herbicide from the point where the herbicide application comes in contact with the leaves of a weed to other parts of the plant including the roots and/or rhizomes. The translocation of an herbicide is an important characteristic which determines whether an herbicide will control a perennial weed, especially if the weed reproduces vegetatively via creeping roots or rhizomes. Glufosinate does not provide good control of perennial weeds as it is not translocated. In summary, glufosinate is not a one-to-one replacement for glyphosate.
Many landscape trees commonly produce vegetative suckers at their trunk base. Suckers are commonly seen on crabapple, flowering cherry, flowering pear, plum, linden, maple and sometimes oak. Honeylocust commonly produces vegetative sprouts along the entire length of their trunk. If these suckers or sprouts are not controlled, the landscape will be a contender for the “Shabby Landscape Award”. Pruning is effective but very time consuming. Another option would be to use the product Scythe that contains pelargonic acid to remove these vegetative suckers and sprouts when they are very small. Very small means less than one inch in length. Pelargonic acid is a contact herbicide. If Scythe is applied to small suckers and sprouts, the product will desiccate them and physical removal will not be required. Larger growth will first need to be physically removed and then Scythe can be used as a maintenance program. Products that contain glyphosate should not be used as glyphosate is a translocated herbicide and injury to the whole tree is possible.
A comment about the use of spray surfactants with herbicide applications. The rule is: “If an herbicide requires the addition of a surfactant, then one should be added per the label. If a surfactant is not required, then one should not be added”. If a required surfactant is not used, the efficacy of the herbicide can be significantly decreased to the point that the herbicide might not work. If a surfactant is added that is not needed, herbicide selectivity can be decreased, leading to with the possibility of injury or death of normally tolerant plants.
Report by Randy Prostak, Weed Specialist, UMass Extension Landscape, Nursery and Urban Forestry Program
Additional Resources
Pesticide License Exams - The MA Dept. of Agricultural Resources (MDAR) is now holding exams online. For more information and how to register, go to: https://www.mass.gov/pesticide-examination-and-licensing.
To receive immediate notification when the next Landscape Message update is posted, join our e-mail list or follow us on Facebook.
For a complete listing of upcoming events, see our upcoming educational events https://ag.umass.edu/landscape/upcoming-events
For commercial growers of greenhouse crops and flowers - Check out UMass Extension's Greenhouse Update website
For professional turf managers - Check out Turf Management Updates
For home gardeners and garden retailers - Check out our home lawn and garden resources.
Diagnostic Services
UMass Laboratory Diagnoses Landscape and Turf Problems - The UMass Extension Plant Diagnostic Lab is available to serve commercial landscape contractors, turf managers, arborists, nurseries and other green industry professionals. It provides woody plant and turf disease analysis, woody plant and turf insect identification, turfgrass identification, weed identification, and offers a report of pest management strategies that are research based, economically sound and environmentally appropriate for the situation. Accurate diagnosis for a turf or landscape problem can often eliminate or reduce the need for pesticide use. For sampling procedures, detailed submission instructions and a list of fees, see Plant Diagnostic Laboratory
Soil and Plant Nutrient Testing - The University of Massachusetts Soil and Plant Nutrient Testing Laboratory is located on the campus of The University of Massachusetts at Amherst. Testing services are available to all. The lab provides test results and recommendations that lead to the wise and economical use of soils and soil amendments. For more information, visit the UMass Soil and Plant Nutrient Testing Laboratory web site. Routine soil analysis and particle size analysis ONLY (no other types of soil analyses available at this time). Turnaround time: Please plan for the fact that date of receipt in the lab is affected by weekends, holidays, shipping time, and time for UMass Campus Mail to deliver samples to the lab. Campus Mail delivery only takes place on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday due to pandemic restrictions.
Tick Testing - The UMass Center for Agriculture, Food, and the Environment provides a list of potential tick identification and testing options at: https://ag.umass.edu/resources/tick-testing-resources.

